Phoenix, Arizona–(Newsfile Corp. – June 9, 2025) – Gunnison Copper Corp. (TSX: GCU) (OTCQB: GCUMF) (FSE: 3XS0) (“Gunnison” or the “Company”) is pleased to announce that mineral processing will commence by July with first copper sales in September at the fully-permitted Johnson Camp Mine (“JCM”), in southeast Arizona.
Progress as of the Company’s last update (see Gunnison news release dated March 21st) included:
- Mining of mineralized material had commenced (Figure 1).
- Material was being stockpiled in advance of the completion of the leach pads (Figure 2).
- Leach pad Phase-1 was complete.
- Phase-2 leach pad was expected in the near term.
Since the Company’s last update, the Company is pleased to report that JCM construction activities are progressing as planned. The haul road to the run of mine oxide Phase-1 pad, PLS sump, culverts and overflow pond construction have started ahead of first acid irrigation. The pipelines from the leach pads to the SX/EW plant are nearing completion, and Phase-1 pad irrigation is anticipated by July, with first copper cathode from Run-of-mine (ROM) production using conventional leach technology scheduled for September. First copper using Nuton technology is expected before the end of the year.

Figure 1 – Mining mineralized material from the JCM pit.
To view an enhanced version of this graphic, please visit:
https://images.newsfilecorp.com/files/2744/254883_ad99f12ba4c1198e_002full.jpg

Figure 2 – Leach Pad Overhead View, 8 million square feet with dimensions of approximately 1220m by 640m. Phase 1 shows the protective, crushed rock, over-liner material on bottom half of the image and Phase 2 shows the crusher pad and Nuton process equipment area. Phase 3 in the upper right corner is the Nuton heap location with liner and overliner being installed.
To view an enhanced version of this graphic, please visit:
https://images.newsfilecorp.com/files/2744/254883_ad99f12ba4c1198e_003full.jpg
“Construction activity continues its fast pace and we are getting ever closer to first irrigation of oxide mine production at JCM SX/EW restart,” states Robert Winton, SVP Operations of Gunnison Copper. He continues, “There is no better time than now to bring a new copper mine online in America, with this critical mineral playing a vital role in our energy and defense security. The efforts of our team and contractors have been second to none during the entire project.”

Figure 3 – New LNG infrastructure storage tank and vaporizers to ensure grade 1 copper production at JCM.
To view an enhanced version of this graphic, please visit:
https://images.newsfilecorp.com/files/2744/254883_ad99f12ba4c1198e_004full.jpg
ABOUT GUNNISON COPPER
Gunnison Copper Corp. is a multi-asset pure-play copper developer and producer that controls the Cochise Mining District (the district), containing 12 known deposits within an 8 km economic radius, in the Southern Arizona Copper Belt.
Its flagship asset, the Gunnison Copper Project, has a measured and indicated mineral resource containing over 831 million tons with a total copper grade of 0.31% (measured mineral resource of 191.3 million tons at 0.37% and indicated mineral resource of 640.2 million tons at 0.29%), and a preliminary economic assessment (“PEA“) yielding robust economics including an NPV8% of $1.3Billion, IRR of 20.9%, and payback period of 4.1 years. It is being developed as a conventional operation with open pit mining, heap leach, and SX/EW refinery to produce finished copper cathode on-site with direct rail link.
The PEA is preliminary in nature and includes inferred mineral resources that are considered too speculative geologically to have the economic considerations applied to them that would enable them to be categorized as mineral reserves. There is no certainty that the conclusions reached in the PEA will be realized. Mineral resources that are not mineral reserves do not have demonstrated economic viability.
In addition, Gunnison’s Johnson Camp Asset, which is under construction with first copper production expected in Q3 2025, is fully funded by Nuton LLC, a Rio Tinto Venture, with a production capacity of up to 25 million lbs of finished copper cathode annually.
Other significant deposits controlled by Gunnison in the district, with potential to be economic satellite feeder deposits for Gunnison Project infrastructure, include Strong and Harris, South Star, and eight other deposits.
For additional information on the Gunnison Project, including the PEA and mineral resource estimate, please refer to the Company’s technical report entitled “Gunnison Project NI 43-101 Technical Report Preliminary Economic Assessment” dated effective November 1, 2024 and available on SEDAR+ at www.sedarplus.ca.
Dr. Stephen Twyerould, Fellow of AUSIMM, President and CEO of the Company is a Qualified Person as defined by NI 43-101. Dr. Twyerould has reviewed and is responsible for the technical information contained in this news release.
For more information on Gunnison, please visit our website at www.GunnisonCopper.com.
ABOUT NUTON
Nuton is an innovative venture that aims to help grow Rio Tinto’s copper business. At the core of Nuton is a portfolio of proprietary copper leaching technologies and capability. Nuton has the potential to economically unlock copper from hard-to-leach ores, including primary sulfides and, in doing so, increase domestic production of critical minerals to support the energy transition. Nuton technologies can achieve market-leading recovery rates and boost copper production in new, ongoing and historical operations, increasing resource utilization and maximizing their value.
With significantly lower energy and water needs than conventional concentrating and smelting, and the ability to produce copper cathode at the mine site, Nuton offers a reliable source of domestically produced copper, with a short mine-to-metal supply chain and the ambition to set industry-leading ESG credentials.
One of the key differentiators of Nuton is the ambition to produce the world’s lightest environmental footprint copper while having at least one Positive Impact at each of its deployment sites, across its five pillars: water, energy, land, materials and society.
For more information, please visit https://nuton.tech.
For further information regarding this press release, please contact:
Gunnison Copper Corp.
Concord Place, Suite 300, 2999 North 44th Street, Phoenix, AZ, 85018
Shawn Westcott
T: 604.365.6681
E: info@GunnisonCopper.com
www.GunnisonCopper.com
Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Information
This news release contains “forward-looking information” concerning anticipated developments and events that may occur in the future. Forward-looking information contained in this news release includes, but is not limited to, statements with respect to: (i) the intention to deploy the Nuton® technology at the Johnson Camp mine and future production therefrom; (ii) the continued funding of the stage 2 work program by Nuton; (iii) the details and expected results of the stage two work program; (iv) timelines for future production and production capacity from the Company’s mineral projects; (v) timelines for continued construction at JCM; (vI) the results of the preliminary economic assessment on the Gunnison Project; and (vIi) the exploration and development of the Company’s mineral projects.
In certain cases, forward-looking information can be identified by the use of words such as “plans”, “expects” or “does not expect”, “budget”, “scheduled”, “estimates”, “forecasts”, “intends”, “anticipates” or “does not anticipate”, or “believes”, or variations of such words and phrases or state that certain actions, events or results “may”, “could”, “would”, “might”, “occur” or “be achieved” suggesting future outcomes, or other expectations, beliefs, plans, objectives, assumptions, intentions or statements about future events or performance. Forward-looking information contained in this news release is based on certain factors and assumptions regarding, among other things, Nuton will continue to fund the stage 2 work program, the availability of financing to continue as a going concern and implement the Company’s operational plans, the estimation of mineral resources, the realization of resource and reserve estimates, copper and other metal prices, the timing and amount of future development expenditures, the estimation of initial and sustaining capital requirements, the estimation of labour and operating costs (including the price of acid), the availability of labour, material and acid supply, receipt of and compliance with necessary regulatory approvals and permits, the estimation of insurance coverage, and assumptions with respect to currency fluctuations, environmental risks, title disputes or claims, and other similar matters. While the Company considers these assumptions to be reasonable based on information currently available to it, they may prove to be incorrect.
Forward-looking information involves known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors which may cause the actual results, performance or achievements of the Company to be materially different from any future results, performance or achievements expressed or implied by the forward-looking information. Such factors include risks related to the Company not obtaining adequate financing to continue operations, Nuton failing to continue to fund the stage 2 work program, the breach of debt covenants, risks inherent in the construction and operation of mineral deposits, including risks relating to changes in project parameters as plans continue to be redefined including the possibility that mining operations may not be sustained at the Gunnison Copper Project, risks related to the delay in approval of work plans, variations in mineral resources and reserves, grade or recovery rates, risks relating to the ability to access infrastructure, risks relating to changes in copper and other commodity prices and the worldwide demand for and supply of copper and related products, risks related to increased competition in the market for copper and related products, risks related to current global financial conditions, risks related to current global financial conditions on the Company’s business, uncertainties inherent in the estimation of mineral resources, access and supply risks, risks related to the ability to access acid supply on commercially reasonable terms, reliance on key personnel, operational risks inherent in the conduct of mining activities, including the risk of accidents, labour disputes, increases in capital and operating costs and the risk of delays or increased costs that might be encountered during the construction or mining process, regulatory risks including the risk that permits may not be obtained in a timely fashion or at all, financing, capitalization and liquidity risks, risks related to disputes concerning property titles and interests, environmental risks and the additional risks identified in the “Risk Factors” section of the Company’s reports and filings with applicable Canadian securities regulators.
Although the Company has attempted to identify important factors that could cause actual actions, events or results to differ materially from those described in forward-looking information, there may be other factors that cause actions, events or results not to be as anticipated, estimated or intended. Accordingly, readers should not place undue reliance on forward-looking information. The forward-looking information is made as of the date of this news release. Except as required by applicable securities laws, the Company does not undertake any obligation to publicly update or revise any forward-looking information.

To view the source version of this press release, please visit https://www.newsfilecorp.com/release/254883
Regulus Resources Inc. (“Regulus” or the “Company”, TSX-V: REG, OTCQX: RGLSF) is pleased to provide an update on the Phase Two metallurgical test program with Nuton LLC (“Nuton”), a Rio Tinto venture. As well, the Company is pleased to provide an update on the integrated resource estimate currently being completed with Compañía Minera Coimolache S.A. (“Coimolache”, collectively with Regulus, the “Parties”), to evaluate the integrated Coimolache Sulphide/AntaKori copper-gold project (“Integrated Sulphide Project”).
Nuton Phase Two Program
The Company continues to work with Nuton to evaluate Nuton’s proprietary sulphide bio-leaching technologies at the AntaKori project. The Phase One program identified that material from AntaKori was amenable to Nuton’s proprietary sulphide bio-leaching technology (see July 6, 2023 press release). In the Phase Two program, a variety of conditions are being evaluated, with each test column using different sets of conditions to evaluate the optimal setup for leaching AntaKori mineralization (particularly enargite-rich high-sulphidation mineralization which makes up the bulk of mineralization at the AntaKori project).
The Company is reporting on the progress of four columns today. Three of the four columns were focused on testing different conditions for enargite-rich high-sulphidation mineralization, while the other column was utilized to test chalcopyrite-dominant porphyry mineralization. The results thus far from the Phase Two program are very encouraging, as Nuton was able to achieve attractive copper extractions utilizing its Nuton bio-leaching technology on both styles of mineralization. As well, this test work has refined the understanding of which set of conditions produces attractive copper extractions for enargite-rich high-sulphidation mineralization. To date, the highest copper extraction for enargite-rich high-sulphidation mineralization is 88.3% (see Figures 1 and 2). To date, the highest copper extraction for porphyry-hosted chalcopyrite mineralization is 87.9% (see Figures 1 and 2). As mentioned previously, this phase of test work is designed to evaluate various conditions to establish the optimum additives for bio-leaching enargite-rich high-sulphidation mineralization. As such, two of the columns identified conditions that produced slower extraction rates and hence less favourable conditions than the column conditions that produced the 88.3% extraction. However, copper extractions in both of these columns continue to trend upwards. Four additional columns have since been started to further refine the optimal conditions achieved and reported here for leaching AntaKori’s enargite-rich high-sulphidation mineralization with Nuton’s bio-leaching technology. The Company will report on these additional columns when they are at or nearing completion.
Integrated Sulphide Project
Regulus and Coimolache, owner of the Tantahuatay oxide gold mine adjacent to the AntaKori project, continue to advance the Integrated Sulphide Project resource estimate. The Parties have worked collaboratively over the past several months to develop an integrated geological model effectively blending views on geology, structure and mineralization styles, which was a critical step before moving towards an integrated resource estimate. The Parties have hired SRK Peru to develop the resource estimate on the Integrated Sulphide Project and it is anticipated that the study will be completed mid-year. As per the agreement between the Parties, the results of this study can only be publicly reported or shared with third parties upon mutual agreement of the Parties.
John Black, Chief Executive Officer of Regulus, commented: “We are very encouraged by the results of the Phase Two program with Nuton. Conditions have been established under which attractive copper extraction is achieved from both high-sulphidation and porphyry mineralization utilizing Nuton’s bio-leaching technology. With several other columns underway, we continue to view Nuton’s bio-leaching technology as one of several potential processing options for mineralization at AntaKori. As well, we have made considerable progress on the integrated resource estimate with Coimolache, with the creation of an integrated geological model. SRK Peru now has all the information they need to complete the resource estimate on the Integrated Sulphide Project and we look forward to receiving the final results soon.”
Qualified Person
The scientific and technical data contained in this news release pertaining to the AntaKori project has been reviewed and approved by Dr. Kevin B. Heather, Chief Geological Officer, FAusIMM, who serves as the qualified person (QP) under the definition of National Instrument 43-101.
ON BEHALF OF THE REGULUS BOARD
(signed) “John Black”
John Black
CEO and Director
Tel: +1 (604) 685-6800
Email: info@regulusresources.com
For further information, please contact:
Regulus Resources Inc.
Ben Cherrington
Tel: +1 347 394 2728
Email: ben.cherrington@regulusresources.com
About Regulus Resources Inc. and the AntaKori Project
Regulus is an international mineral exploration company run by an experienced technical and management team. The principal project held by Regulus is the AntaKori copper-gold-silver project in northern Peru. The AntaKori project currently hosts a resource with indicated mineral resources of 250 million tonnes with a grade of 0.48 % Cu, 0.29 g/t Au and 7.5 g/t Ag and inferred mineral resources of 267 million tonnes with a grade of 0.41 % Cu, 0.26 g/t Au, and 7.8 g/t Ag (independent technical report prepared by AMEC Foster Wheeler (Peru) S.A., a Wood company, titled AntaKori Project, Cajamarca Province, Peru, NI 43-101 Technical Report, dated February 22, 2019 – see news release dated March 1, 2019). Mineralization remains open in most directions.
For further information on Regulus Resources Inc., please consult our website at www.regulusresources.com.
About Nuton
Nuton is an innovative venture that aims to help grow Rio Tinto’s copper business. At the core of Nuton is a portfolio of proprietary copper leaching technologies and capability. Nuton has the potential to economically unlock copper from hard-to-leach ores, including primary sulfides and, in doing so, increase domestic production of critical minerals to support the energy transition. Nuton technologies can achieve market-leading recovery rates and boost copper production in new, ongoing and historical operations, increasing resource utilization and maximizing their value. With significantly lower energy and water needs than conventional concentrating and smelting, and the ability to produce copper cathode at the mine site, Nuton offers a reliable source of domestically produced copper, with a short mine-to-metal supply chain and the ambition to set industry-leading ESG credentials. One of the key differentiators of Nuton is the ambition to produce the world’s lowest footprint copper while having at least one Positive Impact at each of its deployment sites, across its five pillars: water, energy, land, materials and society.
For more information please visit https://nuton.tech.
Forward Looking Information
Certain statements regarding Regulus, including management’s assessment of future plans and operations, may constitute forward-looking statements under applicable securities laws and necessarily involve known and unknown risks and uncertainties, most of which are beyond Regulus’ control. Often, but not always, forward-looking statements or information can be identified by the use of words such as “plans”, “expects” or “does not expect”, “is expected”, “budget”, “scheduled”, “estimates”, “forecasts”, “intends”, “anticipates” or “does not anticipate” or “believes” or variations of such words and phrases or statements that certain actions, events or results “may”, “could”, “would”, “might” or “will” be taken, occur or be achieved.
Specifically, and without limitation, all statements included in this press release that address activities, events or developments that Regulus expects or anticipates will or may occur in the future, including the development of the AntaKori project described herein, and management’s assessment of future plans and operations and statements with respect to the completion of the anticipated exploration and development programs, may constitute forward-looking statements under applicable securities laws and necessarily involve known and unknown risks and uncertainties, most of which are beyond Regulus’ control. These risks may cause actual financial and operating results, performance, levels of activity and achievements to differ materially from those expressed in, or implied by, such forward-looking statements. Although Regulus believes that the expectations represented in such forward-looking statements are reasonable, there can be no assurance that such expectations will prove to be correct. The forward-looking statements contained in this press release are made as of the date hereof and Aldebaran does not undertake any obligation to publicly update or revise any forward-looking statements or information, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, unless so required by applicable securities law.
Neither the TSX Venture Exchange nor its Regulation Services Provider (as that term is defined in policies of the TSX Venture Exchange) accepts responsibility for the adequacy or accuracy of this release.

Figure 1 – Copper deportment by mineral
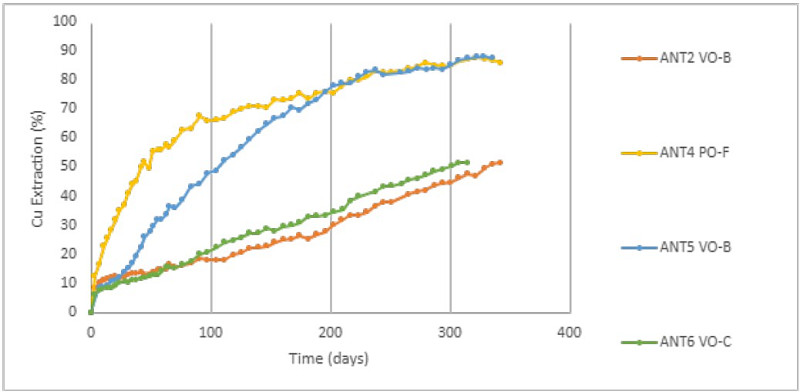
Figure 2 – Copper extractions (VO stands for volcanic-hosted, high-sulphidation, enargite-rich mineralization, PO stands for porphyry-hosted, chalcopyrite-rich mineralization).
“One of Nuton’s goals is to offer a processing technology that not only minimizes water requirements, but ultimately aspires to be water positive, by restoring more water than we consume through our process,” said Yusuf Jameel, PhD, Nuton’s principal sustainability advisor.
Water is one of the five pillars of Nuton’s Positive Impact ambition, and one that could be a “game-changer” for the copper industry, where mines tend to be located in water-stressed areas.
Conventional copper processing technologies require substantial amounts of water, with estimates pegging copper water intensity at around 150m3 (~40,000 gallons) of water per tonne of copper produced (from mine to metal). As Nuton is a copper leaching technology, we have an intrinsic advantage of requiring less water than a concentrator – about a third of it. Nuton as a venture wants to take that advantage to the next level through chasing efficiencies in design, reducing evaporation, reusing wastewater in our process and other opportunities.

Towards water positivity — our North Star
Minimizing the water intensity of Nuton’s process design is an important part of the journey. But the team keeps a focus on its North Star of becoming Water Positive. The team defines being Water Positive as a situation in which we “replenish more water, at least of the same quality, than the water consumed during Nuton’s process.” This is a challenging long-term goal, but the team believes it is one that could strengthen the value proposition of Nuton and the social license of the mining industry.
“One of Nuton’s goals is to offer a processing technology that not only minimizes water requirements, but ultimately aspires to be water positive, by restoring more water than we consume through our process,”
Yusuf Jameel, PhD, Nuton’s principal sustainability advisor.

Charting a water positive path — one step at a time
Every drop of water — even evaporates — matters in Nuton’s process. The current process design aims to minimize water evaporation from the heap through a thermofilm, which acts as a covering blanket and traps moist. By reducing leach pad evaporation, Nuton aims to conserve significant amounts of water, especially important in arid environments like Arizona and Nevada, where some of Nuton’s partners are located. The deployment of Nuton technologies at the Johnson Camp Mine in Arizona, currently under construction, is a prime opportunity to test these and other technical solutions to reduce water intensity and pursue Nuton’s ambition to become water positive.
Nuton’s commitment to sustainability
The Positive Impact Ambition is a core theme in Nuton’s dedication to sustainable mining, with water conservation being a crucial component of that mission. Read about our additional Impact Pillars: Energy, Land, Society and Materials.
Steve McCabe has a packed schedule. As a Senior Deployment Advisor at Nuton, a Rio Tinto venture, his job is to help bring the company’s groundbreaking heap leaching technology to life.
“It’s a lot of coordination,” Steve said, putting it simply.

From working with vendors and leading teams to building mobile labs, and analyzing materials, there’s no shortage of moving pieces ahead of Nuton’s first large-scale deployment at Johnson Camp Mine in Arizona.
Lately, Steve’s main focus has been on agglomeration, a critical step in Nuton’s process. In this phase, fine ore particles are bound together using a blend of additives and solutions, improving permeability and ensuring uniform leaching. This step is essential before the material is placed on heap leach pads, where the bio heap leaching process efficiently extracts copper.
Steve’s passion for his work is evident in his deep knowledge and expertise when discussing his daily responsibilities. He is acutely aware of his journey — from an engineer to a metallurgist to a deployment advisor —and he remains grateful for every step. As the first person in his family to attend college, he understands the significance of higher education.
“There are a lot of challenges that tribal students face,” said Steve, a member of the San Carlos Apache Tribe. For many students in his community, college may not seem likely—or even possible. The reasons are multiple and complex. Some students may not know how to take the next step after high school, while others may feel overwhelmed and unsure of what to do if college is in their plans.
“Many Tribal students underestimate themselves,” Steve explains. “They don’t see their potential. But with the right guidance, they can break through those mental barriers and start seeing what’s out there for them”.
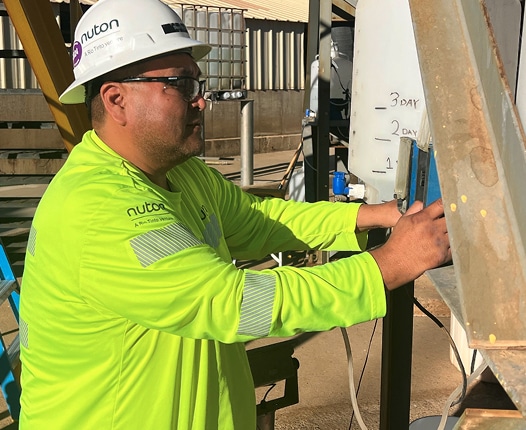

But having a role model—someone who’s been there—can change everything. Before joining Nuton, Steve dedicated years to his Tribe’s education department, assisting students navigate the college process. He continues to mentor high schoolers today, guiding them toward opportunities they might not have realized were within reach.
Steve understands their situation well. When Steve first stepped onto Arizona State University’s campus, he intended to become a nurse. However, after exploring different degree programs, he discovered a passion for chemical engineering. That decision changed his life.
Steve’s education has had a ripple effect—not just for him, but for his entire family. Two of his three children attended Stanford University, and the other recently enrolled at Yale. He doesn’t share this to boast, but to illustrate what’s possible.
“Many Tribal students underestimate themselves,” he explains. “They don’t see their potential. But with the right guidance, they can break through those mental barriers and start seeing what’s out there for them”.
Just like Nuton is working to change the future of copper mining, Steve is working to change the future for students in his community.

Phoenix, Arizona–(Newsfile Corp. – March 3, 2025) – Gunnison Copper Corp. (TSX: GCU) (OTCQB: GCUMF) (FSE: 3XS0) (“Gunnison”) is pleased to announce it has agreed to a non-dilutive funding transaction (the “Nuton Transaction“) with Nuton, LLC (“Nuton“), a Rio Tinto Venture, for $3 million in proceeds to Gunnison to be used toward its costs related to a Nuton testing program at the Gunnison Project, as well as the execution of the Tax Partnership Agreement with an agreed-upon allocation of the potential future proceeds from Gunnison and Nuton’s award of 48C tax credits from the U.S. government. All amounts in this news release are in United States dollars unless otherwise noted.
“The agreement announced today with Nuton provides Gunnison $3 million in non-dilutive financing and the possibility of additional funds during 2025 as result of monetizing the tax credits awarded to Gunnison and Nuton that Gunnison estimates could be up to $8 million,” states Stephen Twyerould, President & CEO of Gunnison. “Nuton’s interest in the Gunnison Copper Project’s sulfide potential and a potential extension to Stage 2 at Johnson Camp are very positive outcomes for the Company.”
Highlights
- Gunnison and Nuton have entered into a Collaboration Agreement that will provide for, among other things:
- Nuton’s exclusivity over novel heap leach processing technologies for sulfide mineralization at the Gunnison Open Pit, and
- Agreed milestones to examine the potential for an extension to the Stage 2 Work Program at the Johnson Camp Mine.
- In exchange for the above:
- Nuton will provide $3M to Gunnison to be used toward its expenses for the Nuton Stage 1 Viability study on the Gunnison Open Pit (expected in early March) and other agreed purposes; and
- The parties will work within the parameters of the Tax Partnership Agreement to allow for a portion of the realized cash proceeds from the potential sale of 48C tax credits to be distributed to Gunnison to benefit the Stage 2 project, including paying down a significant portion, or all of, the Nebari debt. Gunnison estimates that its share of the potential proceeds could be up to $8M after Nuton’s allocation and reimbursement of costs, with the actual amount depending on the 48C tax credit certification process and how much can be realized from the sale of the certified credits.
- In addition to this, Gunnison and Nebari have entered a binding term sheet (details below) that provides for the following:
- Deferral of all principal payments for the remainder of 2025, reducing carrying costs by $2.8M.
- The right to convert up to $6.25M of the principal into equity at a set conversion price based on a premium to market price or financing price.
- A trigger to initiate a process by Nebari to refinance the remaining principal maturity, if any, to December 31, 2029. The trigger occurs when the principal, currently $13.75M (including the Repayment Bonus) is reduced to $7.5M or less (the “Refinance Trigger”).
- The above provides two pathways to trigger the refinancing process, either through Nebari’s conversion of principal to equity, or through funds received under the distribution of money from the potential sale of the 48C tax credits. Should both events occur, or other funds become available, then it is possible that the entire Nebari debt could be extinguished in 2025, which is the objective of Management.
Gunnison Stage 1 Viability Testing
The parties have agreed to conduct a Stage 1 viability testing program of Nuton Technologies on sulfide mineralization at the Gunnison Open Pit (the “Stage 1 Gunnison Program“). The Stage 1 Gunnison Program will involve the collection and testing of samples from drill core from the Gunnison Project. The samples will be analyzed by Nuton for the purposes of determining the suitability of the Gunnison Project with Nuton Technologies.
Stage 2 Extension
Gunnison and Nuton have agreed to work together to evaluate the possible extension of the Stage 2 Work Program at Johnson Camp. This evaluation is guided by a set of milestones and is expected to take place over the next 4 to 6 weeks. Nuton shall also receive a right of first offer over the use of any excess capacity from the SX/EW plant and related infrastructure and mining assets located at the Johnson Camp Mine.
“This initial funding allows us to start evaluating by-product commercialization, increase sulfide production potential through drilling and testing, as well as our mineral optimization program, that are all expected to generate significant value creation. This value creation, in parallel with our Nuton partnered JCM operational ramp up and Q3 scheduled cathode production, are continuing to build Made in America copper,” commented Robert Winton SVP Operations and GM.
Intent to Negotiate Exclusive Exploration Agreement
Gunnison and Nuton (or its affiliates) have also agreed to negotiate in good faith an exclusive exploration agreement over all of Gunnison’s property for a 3-to-5-year term (or such term as agreed between the parties), on commercial terms that includes a specified work program, costs and timelines.
Sale of 48C Tax Credits
As announced on January 16, 2025, Gunnison Copper Corp and Nuton LLC have been selected to receive US$13.9 million in tax credits (the “48C tax credit“) under the Qualifying Advanced Energy Project Credit Program. Nuton and Gunnison will work within the parameters of the Tax Partnership Agreement to potentially allow for a portion of realized cash proceeds from the sale of 48C tax credits to be distributed to Gunnison to retire a significant portion, or all of, the Nebari debt, which will benefit the Stage 2 Work Program by reducing Gunnison’s debt service obligations.
The receipt of the 48C tax credit is subject to Certification as outlined in IRS Notice 2023-44. There is no certainty that the conditions to the completion of the Nuton Transaction or receipt of the 48C tax credit will be satisfied.
Amended and Restated Credit Agreement
Gunnison’s wholly-owned subsidiary Excelsior Mining Arizona, Inc. dba Gunnison Copper (“Gunnison Arizona“) have agreed with Nebari Natural Resources Credit Fund I LP (“Nebari“) to amend certain terms of the Amended and Restated Credit Agreement (the “ARCA“). The amendments provide for, amongst other matters, a suspension of principal amortization from February 1, 2025 until January 1, 2026, provide for potential partial conversion to equity, and provide for a mechanism to repay a portion of the principal amount of the ARCA with proceeds to be received from sale of the previously announced 48C tax credits and through a potential refinancing process provide for an extension of the maturity date.
ARCA Amendments
The Company, Gunnison Arizona and Nebari have signed a binding term sheet (the “Nebari Term Sheet“) setting out the terms for the following amendments to the ARCA (collectively, the “Amendments“):
- Deferral of Principal Amortization: The requirement to begin repaying the principal balance of the ARCA in monthly installments shall be suspended from February 1, 2025 until January 1, 2026. As of January 1, 2026, the remaining principal shall be amortized on a straight-line basis in equal monthly amounts or a monthly amount of $300,000, whichever is smaller.
- Equity Conversion: To provide for a potential alternative repayment mechanism, up to $6.25 million of the principal amount of the ARCA will be convertible, at Nebari’s option, into common shares of Gunnison, at a price (the “Conversion Price“) equal to the lower of (i) a 30% premium to the lowest issuance price of the common shares or units issued in any equity financing prior to March 31, 2025 (subject to minimum pricing rules of the Toronto Stock Exchange); and (ii) the lowest exercise price of any warrants issued as part of any such equity financing, provided that if no equity financing is completed prior to March 31, 2025 the Conversion Price shall be US$0.1622 (Cdn$0.2339), which is a 30% premium to the volume weighted average trading price (“VWAP“) of the common shares of Parent on the Toronto Stock Exchange for the five trading days prior to the execution of the Nebari Term Sheet.
- Principal Reduction through 48C Tax Credit: If Gunnison receives a portion of the cash received from the sale of Johnson Camp 48C tax credit it shall use the lower of $6.25 million or the full amount of the proceeds so received to pay down the non-convertible principal amount of the ARCA.
- Maturity Date Extension: In the event that the principal amount of the ARCA is reduced to $7.5 million or less (whether through conversion or repayment in cash (including cash from the 48C tax credit)), Nebari agrees to seek sale and assignment of the ARCA to another party (the “Loan Buyer“). The assigned ARCA shall have its maturity date amended to 31 December 2029, or such earlier date as agreed between the Loan Buyer and Gunnison, and no amortization shall be due on the convertible portion of the ARCA until the amended maturity date.
- Minimum Cash Balance: The existing financial covenants related to a minimum cash balance and accounts payable aging shall be adjusted so that they only apply to cash and accounts payable that are not related to the Stage 2 Work Program with Nuton, LLC. Furthermore, the required minimum cash balance shall be $1 million.
- Security: Gunnison’s subsidiary Excelsior Mining Holdings, Inc. shall become part of Nebari’s collateral package.
The Amendments are subject to certain conditions including approval of the Toronto Stock Exchange, approval from Greenstone Resources L.P. (“Greenstone“) and Triple Flag, deferral of interest payments due under convertible debentures due to Greenstone and Triple Flag, certain agreements between Nebari and Triple Flag agreement and commencement of a work program by Gunnison to optimize certain opportunities identified in the preliminary economic assessment for the Gunnison Project.
Nebari is at arm’s length to the Company. There are no commissions or finders’ fees payable in connection with the transactions discussed in this news release. While the Nebari Term Sheet is binding, the parties intend to conclude a second amended and restated credit agreement reflecting the terms in the Nebari Term Sheet. There is no assurance that the conditions to the Amendments will be satisfied.
ABOUT GUNNISON COPPER
Gunnison Copper Corp. is a multi-asset pure-play copper developer and producer that controls the Cochise Mining District (the district), containing 12 known deposits within an 8 km economic radius, in the Southern Arizona Copper Belt.
Its flagship asset, the Gunnison Copper Project, has a measured and indicated mineral resource containing over 831 million tons with a total copper grade of 0.31% (measured mineral resource of 191.3 million tons at 0.37% and indicated mineral resource of 640.2 million tons at 0.29%), and a preliminary economic assessment (“PEA“) yielding robust economics including an NPV8% of $1.3Billion, IRR of 20.9%, and payback period of 4.1 years. It is being developed as a conventional operation with open pit mining, heap leach, and SX/EW refinery to produce finished copper cathode on-site with direct rail link.
The PEA is preliminary in nature and includes inferred mineral resources that are considered too speculative geologically to have the economic considerations applied to them that would enable them to be categorized as mineral reserves. There is no certainty that the conclusions reached in the PEA will be realized. Mineral resources that are not mineral reserves do not have demonstrated economic viability.
In addition, Gunnison’s Johnson Camp Asset, which is under construction with first copper production expected in mid 2025, is fully funded by Nuton LLC, a Rio Tinto Venture, with a production capacity of up to 25 million lbs of finished copper cathode annually.
Other significant deposits controlled by Gunnison in the district, with potential to be economic satellite feeder deposits for Gunnison Project infrastructure, include Strong and Harris, South Star, and eight other deposits.
For additional information on the Gunnison Project, including the PEA and mineral resource estimate, please refer to the Company’s technical report entitled “Gunnison Project NI 43-101 Technical Report Preliminary Economic Assessment” dated effective November 1, 2024 and available on SEDAR+ at www.sedarplus.ca.
Dr. Stephen Twyerould, Fellow of AUSIMM, President and CEO of the Company is a Qualified Person as defined by NI 43-101. Mr. Twyerould has reviewed and is responsible for the technical information contained in this news release.
For more information on Gunnison, please visit our website at www.GunnisonCopper.com.
ABOUT NUTON
Nuton, a subsidiary of Rio Tinto, is an innovative venture focused on finding better ways to produce the copper the world needs with the smallest possible environmental footprint. At the core of Nuton is a portfolio of proprietary nature-based leaching technologies and capabilities that offer the potential to economically unlock copper through bio-heap leaching, including from primary sulfide resources, achieving market-leading recovery rates and increasing copper production at new and ongoing operations. One of the key differentiators of Nuton is our ambition to produce the world’s lowest carbon footprint copper while having at least one Positive Impact at each deployment site across five pillars: water, energy, land, materials and society.
To learn more about Nuton, visit https://nuton.tech/
For further information regarding this press release, please contact:
Gunnison Copper Corp.
Concord Place, Suite 300, 2999 North 44th Street, Phoenix, AZ, 85018
Shawn Westcott
T: 604.365.6681
E: info@GunnisonCopper.com
www.GunnisonCopper.com
Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Information
This news release contains “forward-looking information” concerning anticipated developments and events that may occur in the future. Forward looking information contained in this news release includes, but is not limited to, statements with respect to: (i) the intention to deploy the Nuton® technology at the Johnson Camp mine and future production therefrom; (ii) the continued funding of the stage 2 work program by Nuton; (iii) the details and expected results of the stage two work program; (iv) future production and production capacity from the Company’s mineral projects; (v) the results of the preliminary economic assessment on the Gunnison Project; (vi) the exploration and development of the Company’s mineral projects; (vii) the satisfaction of final conditions and receipt of 48C tax credits; (viii) the terms of the Nuton Transaction; (ix) the terms of the Amendments; and (xi) the satisfaction of the conditions to the Nuton Transaction and the Amendments.
In certain cases, forward-looking information can be identified by the use of words such as “plans”, “expects” or “does not expect”, “budget”, “scheduled”, “estimates”, “forecasts”, “intends”, “anticipates” or “does not anticipate”, or “believes”, or variations of such words and phrases or state that certain actions, events or results “may”, “could”, “would”, “might”, “occur” or “be achieved” suggesting future outcomes, or other expectations, beliefs, plans, objectives, assumptions, intentions or statements about future events or performance. Forward-looking information contained in this news release is based on certain factors and assumptions regarding, among other things, Nuton will continue to fund the stage 2 work program, Nuton and Gunnison will execute definitive agreements for the Nuton Transaction, Gunnison and Nebari will execute definitive agreements for the Amendments, the availability of financing to continue as a going concern and implement the Company’s operational plans, the allocation of the 48C tax credits between the Company and Nuton, the satisfaction of the requirements set forth in Section 48C of the Internal Revenue Code, the estimation of mineral resources, the realization of resource and reserve estimates, , copper and other metal prices, the timing and amount of future development expenditures, the estimation of initial and sustaining capital requirements, the estimation of labour and operating costs (including the price of acid), the availability of labour, material and acid supply, receipt of and compliance with necessary regulatory approvals and permits, the estimation of insurance coverage, and assumptions with respect to currency fluctuations, environmental risks, title disputes or claims, and other similar matters. While the Company considers these assumptions to be reasonable based on information currently available to it, they may prove to be incorrect.
Forward looking information involves known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors which may cause the actual results, performance or achievements of the Company to be materially different from any future results, performance or achievements expressed or implied by the forward-looking information. Such factors include risks related to the Company not obtaining adequate financing to continue operations, Nuton and Gunnison failing to conclude definitive agreements for the Nuton Transaction, Nebari and Gunnison failing to conclude definitive agreements for the Amendments, Nuton failing to continue to fund the stage 2 work program, the failure to satisfy the requirements set forth in Section 48C of the Internal Revenue Code, 100% of the 48C tax credits may be allocated to repay capital expenditures for the Johnson Camp mine, the breach of debt covenants, risks inherent in the construction and operation of mineral deposits, including risks relating to changes in project parameters as plans continue to be redefined including the possibility that mining operations may not be sustained at the Gunnison Copper Project, risks related to the delay in approval of work plans, variations in mineral resources and reserves, grade or recovery rates, risks relating to the ability to access infrastructure, risks relating to changes in copper and other commodity prices and the worldwide demand for and supply of copper and related products, risks related to increased competition in the market for copper and related products, risks related to current global financial conditions, risks related to current global financial conditions on the Company’s business, uncertainties inherent in the estimation of mineral resources, access and supply risks, risks related to the ability to access acid supply on commercially reasonable terms, reliance on key personnel, operational risks inherent in the conduct of mining activities, including the risk of accidents, labour disputes, increases in capital and operating costs and the risk of delays or increased costs that might be encountered during the construction or mining process, regulatory risks including the risk that permits may not be obtained in a timely fashion or at all, financing, capitalization and liquidity risks, risks related to disputes concerning property titles and interests, environmental risks and the additional risks identified in the “Risk Factors” section of the Company’s reports and filings with applicable Canadian securities regulators.
Although the Company has attempted to identify important factors that could cause actual actions, events or results to differ materially from those described in forward-looking information, there may be other factors that cause actions, events or results not to be as anticipated, estimated or intended. Accordingly, readers should not place undue reliance on forward-looking information. The forward-looking information is made as of the date of this news release. Except as required by applicable securities laws, the Company does not undertake any obligation to publicly update or revise any forward-looking information.

To view the source version of this press release, please visit https://www.newsfilecorp.com/release/243016
Jeana Ratcliff, who works as a Senior Sustainability Advisor at Nuton, a Rio Tinto venture, was born to be a scientist. Growing up in Montana, she spent her childhood outdoors with her science-minded parents, rock-hounding and learning about geology.
Her curiosity extended indoors, where – she constantly tinkered with electronics, learning the ins and outs of any machine she could get her hands on. Jeana fondly recalls buying an old keyboard, taking it apart, and attempting to reassemble it with her two sisters. Her inquisitive nature and love for learning have persisted into her current role at Nuton.
In celebration of International Day of Women and Girls in Science, Jeana shared insights about her career journey in the sciences, lessons learned along the way, and the advice she would offer others, especially women, considering a career in science.

What does a typical day at Nuton look like for you?
That’s a big question (laughs). Nuton is very dynamic, we’re growing and changing everyday. My focus on sustainability is really Nuton’s overall mission; to produce copper with a positive impact. I’m lucky to be involved in bringing that vision to life.
Most of my work is to directly engage and interface with our partners. I assess where their operations currently are, and how we can explore further opportunities to improve performance through Nuton. We like to challenge the status quo by asking ‘How do we move forward in creating a more sustainable kind of copper supply chain?’
Day to day, my work is quite varied. It’s a good mix of relationship building and data management, and I get to spend some time out in the field every now and then. I enjoy getting out there and being able to see operations, boots on the ground.
Do you like your job?
Yes! Mining is very interesting. You touch every science discipline in this industry. Especially the environmental sciences but also there’s water, biology, chemistry, electrical, mechanical; there’s sort of a piece of every kind of science. I learn a lot every day, which is fun.


How did you first become interested in this particular field?
Most of my family is in the mining industry. My dad is a geophysicist, my mom is a geological engineer. It’s funny, when I first got to college I wanted to explore other careers, but I ended up with a degree in civil engineering and land rehabilitation and found my way back to mining. It’s just fun and super dynamic! Much of my interest had to do with the exposure that I had growing up with my family and the things that we did together. This work is fun, I like it, and I feel like I’m good at it.
What kind of science or mining activities did you and your family do when you were young?
We loved going out to do small-scale prospecting or rock-hounding even. For much of my childhood, my mom was working on mine sites, so having that female role model was huge. What she was doing while being a mother to our family was just a normal thing for me. It didn’t feel like there was a barrier to being a woman doing science-related work. I was like, ‘Oh, Mom’s doing it, so off we go.’


What does it mean to young women to have a role model to look up to in your industry?
I think it’s huge. The classic saying is, if you see it, you can be it. I think that that’s true for a lot of people. Sometimes in the mining industry, there’s still this perception of who does that kind of work. To work in the mining industry does not mean that you’re the guy in the tunnel with the pick axe. Those jobs do exist in some places, but there’s so much more out there.
Having women in leadership positions and different roles can help others understand that there are many different paths to being successful in mining.

What’s your message to young females considering a science-related profession, perhaps in mining specifically?
I think my biggest message is that you don’t have to know everything, and you don’t have to be perfect. A lot of engineers, and scientists, particularly women, struggle with this.
Even as you get further into your career, you should still be learning. There’s a lot of imposter syndrome or fear of asking questions, but I recommend just being curious and allowing yourself to learn more and come up with new ideas. It can feel vulnerable. But realize you don’t have to be 100% perfect at everything to have success.
Casa Grande, AZ and Toronto, ON, January 31, 2025 – Arizona Sonoran Copper Company Inc. (TSX:ASCU | OTCQX:ASCUF) (“ASCU” or the “Company”), an emerging US copper developer, is pleased to announce that further to its press release dated January 9, 2025 (the “January 9 PR”), it has closed its private placement with Hudbay Minerals Inc. (“Hudbay”) of 11,955,270 common shares at a price of C$1.68 for gross proceeds to the Company of C$20,084,853 million (the “Hudbay Placement”). Additionally, Nuton LLC (“Nuton”), a Rio Tinto Venture, exercised its pre-emptive rights in respect of the Hudbay Placement, pursuant to the terms of its investor rights agreement, to maintain its 7.2% equity interest in the Company for gross proceeds of C$1,562,210 (the “Nuton Placement”). Pursuant to the Hudbay Placement and the Nuton Placement, the Company issued a total of 12,885,157 common shares at a price of C$1.68 per share for aggregate gross proceeds of C$21,647,064 to the Company (the “Private Placement”). The subscription by Hudbay reflects the base offering of 11,852,064 common shares as well as top-up shares of 103,206 common shares to achieve its 9.99% ownership of the Company after giving effect to the Private Placement.
ASCU President and CEO, George Ogilvie commented, “With the completion of this financing, our company is fully funded with additional runway to complete our 2025 work programs. Our main deliverable in 2025 is the preparation of updated technical data on the entire Parks/Salyer deposit and producing a Pre-Feasibility Study in the second half of the year. We are excited to welcome Hudbay as a strategic investor of the Company; an endorsement by a well-known and sophisticated entity. Hudbay has significant experience in mine development and construction, and we look forward to tapping into that wealth of knowledge as we continue to de-risk the Cactus Project through the remaining study phases to an eventual final investment decision, followed by construction and development. We also value the ongoing support of and partnership with Nuton.”
Concurrent with the closing of the Hudbay Placement, ASCU and Hudbay executed an investor rights agreement substantially on the terms disclosed in the January 9 PR. A copy of the investor rights agreement will be available in due course on SEDAR+ (www.sedarplus.ca) under the Company’s issuer profile.
Proceeds of the Private Placement are to be allocated for drilling, exploration, technical studies advancement of the Company’s Cactus Project, and for general corporate purposes.
The common shares issued under the Private Placement are subject to a statutory hold period under applicable Canadian securities laws, expiring four months after closing the transaction. The Private Placement is subject to the final approval of the Toronto Stock Exchange.
Scotiabank acted as financial advisor, and Bennett Jones LLP as legal advisor, to the Company, in connection with the Private Placement.
Neither the Toronto Stock Exchange nor the regulating authority has approved or disproved the information contained in this press release.
About Arizona Sonoran Copper Company (www.arizonasonoran.com | www.cactusmine.com)
ASCU is a copper exploration and development company with a 100% interest in the brownfield Cactus Project. The Project, on privately held land, contains a large-scale porphyry copper resource and a recent PEA proposes a generational open pit copper mine with robust economic returns. Cactus is a lower risk copper developer benefitting from a state-led permitting process, in place infrastructure, highways and rail lines at its doorstep and onsite permitted water access. The Company objective is to develop Cactus and become a mid-tier copper producer with low operating costs, that could generate robust returns and provide a long-term sustainable and responsible operation for the community, investors and all stakeholders. The Company is led by an executive management team and Board which have a long-standing track record of successful project delivery in North America complemented by global capital markets expertise.
For more information
Alison Dwoskin, Director, Investor Relations
647-233-4348
adwoskin@arizonasonoran.com
George Ogilvie, President, CEO and Director
416-723-0458
gogilvie@arizonasonoran.com
Cautionary Statements regarding Forward-Looking Statements and Other Matters
Forward-Looking Statements
All statements, other than statements of historical fact, contained or incorporated by reference in this press release constitute “forward-looking statements” and “forward-looking information” (collectively, “forward-looking statements”) within the meaning of applicable Canadian and United States securities legislation. Generally, these forward-looking statements can be identified by the use of forward-looking terminology such as “advancement”, “assumptions”, “become”, “continue”, “could”, “deliverable”, “delivery”, “develop”, “development”, “emerging”, “estimates”, “expected”, “exploration”, “eventual”, “feasibility”, “followed”, “forward”, “future”, “generational”, “going”, “long-term”, “looking”, “near-term”, “objective”, “phases”, “plan”, “proposes”, “risk”, “runway”, “study”, “subject to”, “to be”, and “upgrading”, or variations of such words, and similar such words, expressions or statements that certain actions, events or results can, could, may, should, would, will (or not) be achieved, occur, provide, result or support in the future, or which, by their nature, refer to future events. In some cases, forward-looking information may be stated in the present tense, such as in respect of current matters that may be continuing, or that may have a future impact or effect. Forward-looking statements include the use of proceeds of the Private Placement; the timing and ability of the Company to receive final approval of the Toronto Stock Exchange in respect of the Private Placement; the advancement and future of the Cactus Project (including the 2025 work programs and other operations, copper production, returns (economic or otherwise)); the PEA and results thereof; the preparation of an updated technical data on Parks/Salyer (including the timing thereof); the amount of funding required to complete the 2025 work program; the completion and delivery of a Pre-Feasibility Study and other studies on the Cactus Project (including the timing thereof); any eventual investment decision on, or development or construction of the Cactus Project; copper resource at the Cactus Project; permitting; operating costs; any upside in value and/or delivered back to shareholders, sustainability and risk; the Company’s objectives (including the Cactus Project becoming a significant producer of copper cathodes in Arizona and the U.S.); the future plans or prospects of the Company (including sustainability of the Cactus Project and becoming a mid-tier copper producer); and the impact of Hudbay’s and Nuton’s investment and support in respect of the Company and its projects. Although the Company believes that such statements are reasonable, there can be no assurance that those forward-looking statements will prove to be correct, and any forward-looking statements by the Company are not guarantees of future actions, results or performance. Forward-looking statements are based on assumptions, estimates, expectations and opinions, which are considered reasonable and represent best judgment based on available facts, as of the date such statements are made. If such assumptions, estimates, expectations and opinions prove to be incorrect, actual and future results may be materially different than expressed or implied in the forward-looking statements. The assumptions, estimates, expectations and opinions referenced, contained or incorporated by reference in this press release which may prove to be incorrect include those set forth or referenced in this press release, as well as those stated in the technical report for the Cactus Project filed on August 27, 2024 (the “2024 PEA Technical Report”), the Company’s Annual Information Form dated April 1, 2024 (the “AIF”), Management’s Discussion and Analysis (together with the accompanying financial statements) for the year ended December 31, 2023 and the quarters already ended in 2024 (collectively, the “2023-24 Financial Disclosure”) and the Company’s other applicable public disclosure (collectively, “Company Disclosure”), all available on the Company’s website at www.arizonasonoran.com and under its issuer profile at www.sedarplus.ca. Forward-looking statements are inherently subject to known and unknown risks, uncertainties, contingencies and other factors which may cause the actual results, performance or achievements of ASCU to be materially different from any future results, performance or achievements expressed or implied by the forward-looking statements. Such risks, uncertainties, contingencies and other factors include, among others, the “Risk Factors” in the AIF, and the risks, uncertainties, contingencies and other factors identified in the 2024 PEA Technical Report and the 2023-24 Financial Disclosure. The foregoing list of risks, uncertainties, contingencies and other factors is not exhaustive; readers should consult the more complete discussion of the Company’s business, financial condition and prospects that is provided in the AIF, the 2023-24 Financial Disclosure and other Company Disclosure. Although ASCU has attempted to identify important factors that could cause actual actions, events or results to differ materially from those described in forward-looking statements, there may be other factors that cause actions, events or results to differ from those anticipated, estimated or intended. Forward-looking statements contained herein are made as of the date of this press release (or as otherwise expressly specified) and ASCU disclaims any intention or obligation to update or revise any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or results or otherwise, except as required by applicable securities laws. There can be no assurance that such information will prove to be accurate, as actual results and future events could differ materially from forward-looking statements. Accordingly, readers should not place undue reliance on forward-looking statements. The forward-looking statements referenced or contained in this press release are expressly qualified by these Cautionary Statements as well as the Cautionary Statements in the AIF, the 2024 PEA Technical Report, the 2023-24 Financial Disclosure and other Company Disclosure.
Preliminary Economic Assessments
The Preliminary Economic Assessment (or PEA) referenced in this press release and summarized in the 2024 PEA Technical Report is only a conceptual study of the potential viability of the Cactus Project and the economic and technical viability of the Cactus Project has not been demonstrated. The PEA is preliminary in nature and provides only an initial, high-level review of the Cactus Project’s potential and design options; there is no certainty that the PEA will be realized. For further detail on the Cactus Project and the PEA, including applicable technical notes and cautionary statements, please refer to the Company’s press release dated August 7, 2024 and the 2024 PEA Technical Report, both available on the Company’s website at www.arizonasonoran.com and under its issuer profile at www.sedarplus.ca.
Mineral Resource Estimates
Until mineral deposits are actually mined and processed, copper and other mineral resources must be considered as estimates only. Mineral resource estimates that are not classified as mineral reserves do not have demonstrated economic viability. The estimation of mineral resources is inherently uncertain, involves subjective judgement about many relevant factors and may be materially affected by, among other things, environmental, permitting, legal, title, taxation, socio-political, marketing, or other known and unknown risks, uncertainties, contingencies and other factors described in the foregoing Cautionary Statements on Forward-Looking Statements. The quantity and grade of reported “inferred” mineral resource estimates are uncertain in nature and there has been insufficient exploration to define “inferred” mineral resource estimates as an “indicated” or “measured” mineral resource and it is uncertain if further exploration will result in upgrading “inferred” mineral resource estimates to an “indicated” or “measured” mineral resource category. Inferred mineral resource estimates may not form the basis of feasibility or pre-feasibility studies or economic studies except for preliminary economic assessments. The accuracy of any mineral resource estimate is a function of the quantity and quality of available data, and of the assumptions made and judgments used in engineering and geological interpretation, which may prove to be unreliable and depend, to a certain extent, upon the analysis of drilling results and statistical inferences that may ultimately prove to be inaccurate. It cannot be assumed that all or any part of a “inferred”, “indicated” or “measured” mineral resource estimate will ever be upgraded to a higher category including a mineral reserve. The mineral resource estimates declared by the Company were estimated, categorized and reported using standards and definitions in accordance with the Canadian Institute of Mining, Metallurgy and Petroleum Definition Standards for Mineral Resources and Mineral Reserves (the “CIM Standards”) in accordance with National Instrument 43-101 of the Canadian Securities Administrators (“NI 43-101”), which governs the public disclosure of scientific and technical information concerning mineral projects.
U.S. Readers
The terms “mineral resource”, “measured mineral resource”, “indicated mineral resource” and “inferred mineral resource” as disclosed by the Company are Canadian mining terms defined in the CIM Standards (collectively, the “CIM Definitions”) in accordance with NI 43-101. NI 43-101 establishes standards for all public disclosure that a Canadian issuer makes of scientific and technical information concerning mineral projects. These Canadian standards differ from the requirements of the United States Securities and Exchange Commission (the “SEC”) applicable to United States domestic and certain foreign reporting companies under Subpart 1300 of Regulation S-K (“S-K 1300”). Accordingly, information describing mineral resource estimates for the Cactus Project may not be comparable to similar information publicly reported in accordance with the applicable requirements of the SEC, and so there can be no assurance that any mineral resource estimate for the Cactus Project would be the same had the estimates been prepared per the SEC’s reporting and disclosure requirements under applicable United States federal securities laws, and the rules and regulations thereunder, including but not limited to S-K 1300. Further, there is no assurance that any mineral resource or mineral reserve estimate that the Company may report under NI 43-101 would be the same had the Company prepared such estimates under S-K 1300.
