A penny for your thoughts? Not without copper. Copper is an essential metal that serves seemingly endless purposes in the modern world—often unnoticed but indispensable. Batteries. Pipes. Wiring. And, yes, pennies. The metal exists almost everywhere. Its versatility can be found in things as ubiquitous as jewelry and electronics to advanced lifesaving medical equipment, making it a true cornerstone of everyday life.

Copper is more ubiquitous than ever, making sustainable mining practices pivotal to ensuring continued availability and reducing environmental impacts. Ventures like Nuton are so important to the future of copper mining, utilizing technologies like bioheap leaching that simultaneously help meet the massive demand for copper while minimizing environmental impact.
How Copper is Used in Our Daily Lives
Imagine a typical day; as you brew your coffee, copper pipes ensure that water flows safely through your coffee maker, delivering your morning buzz. During your morning commute, the car’s electronics and motors rely on copper to power the engine. Smartphones and computers, containing intricate copper circuitry, keep you connected to the world. The electrical grid and telecommunications network – even the satellites orbiting Earth – all rely on copper wire and components to connect calls. Later, as you prepare dinner, copper cookware evenly distributes heat to your food. From dawn to dusk, copper presents itself in countless ways. This reddish-brown metal appears in ways you might not immediately recognize.

Top Uses for Copper
Copper finds myriad applications across various industries due to its unique properties. Its conductivity, durability, malleability, and antimicrobial nature make it indispensable to many industries. Here are some key ways copper is used across different sectors:
Reliable Power Transmission in Electrical Applications
Copper provides the foundation for power transmission systems; it is a premier conductor of electricity, second only to silver. Its extensive application in copper wire, transformers, and electrical grids ensures the seamless flow of energy, which is vital for powering our communities.
Moreover, copper’s role extends to the intricate circuitry of printed circuit boards (PCBs) within electronic devices, where its conductivity allows efficient energy transfer and reliable performance. Copper is even essential in components used by electrical engineers, like busbars, electric motors, switch gears, and circuit breakers.
Antimicrobial Control, Power Transmission, and Radio Frequency Shielding in Medical Application
Copper is a crucial element in the medical field, serving multiple purposes. Its antimicrobial properties make it useful for creating surfaces that aid in infection control within healthcare settings; some hospitals are starting to adopt antimicrobial copper touch surfaces to help create sterile environments.
Additionally, copper’s durability and biocompatibility make it an optimal choice for crafting medical instruments and tools. Copper circuitry delivers power to medical electronics, contributing to their functionality and reliability.
Furthermore, in advanced medical technologies like MRI rooms, copper is sometimes utilized in radio frequency shielding that lines the walls and ceilings. Copper even helps power active implantable medical devices, extending the lives of millions.
Thermal Conductivity and Energy Conversion in Industrial Machinery
Copper’s properties lend themselves to crucial applications in industrial machinery and enhance efficiency in various industrial processes. Delocalized electrons within copper’s solid lattice structure have the freedom to move unrestricted, effectively transporting heat. This unique property transforms copper into a highly efficient conductor, facilitating heat flow across its surface. This exceptional thermal conductivity makes it indispensable in regulating temperature in heat exchangers.
Copper plays a pivotal role in electric motors and generators, facilitating efficient energy conversion and powering essential machinery for production and operation. Copper enables countless industrial machines—hydraulic presses, mills, cement mixers, and high-power lasers—to operate more efficiently.
Longevity and Weather-Resistance in Construction Materials
Copper is a versatile construction material with numerous applications. Copper pipes ensure durable and reliable plumbing systems, while copper roofing materials provide weather-resistant solutions that protect structures and enhance architectural aesthetics. Copper does not rust, but it will develop a patina and darken over time when exposed to the elements. Due to its malleability and corrosion resistance, the metal is utilized in architectural elements like railings and gutters. Its applications extend to artistic sculptures and, statue building. We can all name at least one very famous and iconic statue made from copper.
Other Applications: Jewelry, Tools, Musical Instruments, and More
These top uses for copper only scratch the surface. There are seemingly endless applications for copper, ranging from jewelry-making to tool manufacturing. Its aesthetic appeal and durability make it ideal for crafting intricate designs and sturdy equipment like cookware and heat sinks. In musical instruments, copper alloys like brass contribute to creating distinctive tones, enriching musical experiences. Copper is also important for currency production and textile manufacturing.
Sustainable Copper Mining Facilitates a Better Future
As demand for copper increases, it becomes crucial to ensure our access to copper is sustainable. Innovations in mining technologies, such as those pioneered by Nuton, are at the forefront of this endeavor, striving to meet the growing demand for copper while minimizing its ecological footprint.
To discover more about Nuton’s transformative technologies and their impact on the industry, delve deeper into the Nuton process and explore the possibilities for a sustainable future.
Casa Grande, AZ and Toronto, ON, June 10, 2024 – Arizona Sonoran Copper Company Inc. (TSX:ASCU | OTCQX:ASCUF) (“ASCU” or the “Company”) reports drilling results targeting below the leachable oxides and enriched sulphides, into the untested extents of primary copper mineralization around the Cactus West Pit, on the Cactus Project, in Arizona. Drilling confirms a thick zone of primary sulphide mineralization beneath the Cactus West open pit mine plan and at least 750 ft (229 m) south, 500 ft (152 m) southwest and up to an additional 700 ft (213 m) below the Cactus West mineral resource shell (see FIGURES 1-8). The program is part of the 2024 Nuton Work Program sponsored by Nuton LLC, a Rio Tinto venture, as announced January 30, 2024.
A total of 5 drill holes are reported herein for a total of 8,366 ft (2,550 m). The Nuton-sponsored drill program aims to further delineate the primary mineralization beneath the existing oxides and enriched sulphides at the Cactus West open pit, as outlined in the current mine plan. Additionally, the program seeks to extend exploration efforts to the south and southwest regions. The program follows up on geotechnical hole ECW-150 (see PR January 10, 2024), which also encountered a significant primary sulphide interval, extending mineralization by 674 ft (205 m) below the mineral resource shell, within a total interval of 1,416 ft (432 m) @ 0.45% CuT.
Drilling Highlights
- ECW-246*: 1,463 ft (446 m) @ 0.31% CuT of continuous mineralization
- 1,370 ft (418 m) @ 0.31% CuT, 0.004% Mo (primary)
- ECW-243: 987 ft (301 m) @ 0.34% CuT of continuous mineralization
- 191 ft (58 m) @ 0.35% CuT, 0.30% Cu TSol, 0.014% Mo (enriched)
- 796 ft (243 m) @ 0.33% CuT, 0.011% Mo (primary)
- ECW-245: 1,033 ft (315 m) @ 0.28% CuT of continuous mineralization
- 190 ft (58 m) @ 0.56% CuT, 0.010% Mo (primary)
- ECW-241: 852 ft (260 m) @ 0.38% CuT of continuous mineralization
- 316 ft (96 m) @ 0.34% CuT, 0.27% Cu TSol, 0.005% Mo (enriched) from 132 m depth
- 536 ft (163 m) @ 0.39% CuT, 0.019% Mo (primary)
NOTE: True widths are not known; * Hole terminated in primary mineralization and angled at –47.5° dip, all other holes drilled vertical and terminated in the basement fault
George Ogilvie, Arizona Sonoran President and CEO commented, “While our engineering and geology teams remain focused on the integration of our MainSpring property into our February 2024 Pre-Feasibility Study, our geo teams continue their exemplary low discovery cost programs. To date, the discovery cost on our Cactus porphyry is under $0.01/lb, and therefore telling us to continue drilling until that cost begins to increase.”
He continued, “The Cactus 2024 drilling programs focused on MainSpring infill drilling and expansion drilling at Cactus West. MainSpring presents engineering with the opportunity to improve economics at Parks/Salyer. At Cactus West, the team is targeting below the previously known mineral extents within the primary sulphides for future opportunities and optionality. Cactus infill drilling is returning wide intervals of primary copper mineralization both below the open pit mine plan, and also outside of the current mineral resource shell. While these Cactus West results will not be included in the pending Preliminary Economic Assessment, we see an expanding primary sulphide zone as future optionality on what is already one of the largest development stage Copper assets in the United States today.”
Drilling Recap
The Cactus West infill and exploration drill program as announced in the January 30, 2024 work plan press release and as part of the 2024 Nuton Work Program, supports the expansion of primary sulphide mineralization, particularly near ECW-150 and is ongoing with two drills. The current drilling will not be reflected in the pending Preliminary Economic Assessment.
Previously, most drilling at Cactus West crossed through the oxide and enriched zones prior to terminating in the upper portions of the primary sulphide mineralization. This developed the oxide and enriched copper resources to support a conventional heap leach project. The current drill program at Cactus West targets the untested extents of primary mineralization by drilling completely through the enriched and primary mineralization zones to the basement fault and stopping in the rock units that compose the basement complex. This drilling is confirming a thick zone of primary mineralization beneath the thinner enrichment zone, typically followed by a barren granitic unit at depth above the basement fault. Though the drill program is in the early stages, it has confirmed that a thick zone of primary mineralization extends beneath the Cactus West pit as well as at least 750 feet south and 500 feet southwest of the pit. Results to date show primary sulphide copper grade increasing from east to west across the southern side of the pit. Grades are interpreted to increase further on the southwest corner of the pit as the drilling aligns with the historical mine trend, consistent with results previously reported from ECW-150. The program will continue to test the extents of primary mineralization to the south and southwest, as it also works to in-fill the areas under and immediately adjacent to the Cactus West pit.
The oxide and enriched proven and probable reserve at Cactus West totals 75.5 Mtons @ 0.26% Cu TSol for 463 Mlbs of copper. Within the Pre-Feasibility Study, Cactus West contributes approximately 12 Mtons annually within the first 7 years of production as an open pit layback. Meanwhile, the Cactus West and East primary sulphide mineral resource estimate consists of 72.9 Mtons @ 0.34% CuT M&I for 463M lbs of copper and 120.4 Mtons @ 0.34% CuT for 837 Mlbs of copper inferred, inclusive of Cactus East (see PR dated February 21, 2024for notes and disclaimers related to the reserves and resources). The Cactus Project overall, inclusive of Parks/Salyer, contains 446 Mtons @ 0.58% CuT for 5.2 Blbs measured and indicated and 224 Mtons @ 0.472% CuT for 2.2 Blbs inferred.
Table 1: Significant Drilling Intercepts
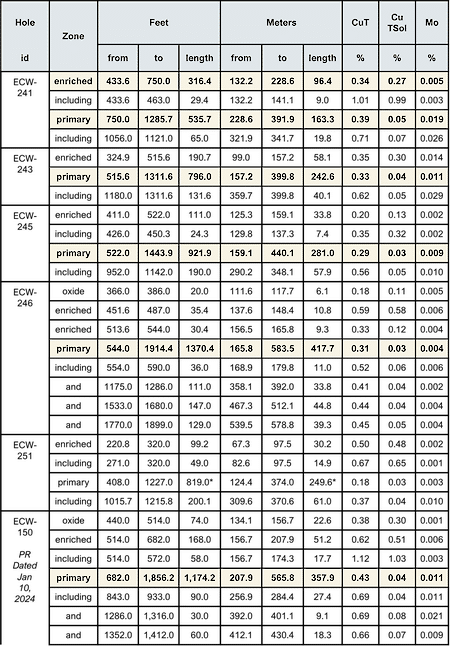
- Intervals are presented in core length and are drilled vertically, except in the case of ECW-246 at –47.5°.
- Drill assays assume a mineralized cut-off grade of 0.1% CuT reflecting the potential for heap leaching of open pit material in the case of Oxide and Enriched or in the case of Primary material to provide typical average grades. Holes were terminated below the basement fault except in the case of hole ECW-246.
- Assay results are not capped. Intercepts are aggregated within geological confines of major mineral zones.
- * Includes 10.3 ft (3.2 m) of missing core
- True widths are not known
Table 2: Drilling Details
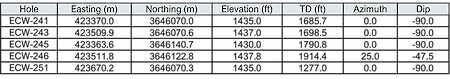
Note: Drill locations are based on drill plans and hand-held GPS locators and may be adjusted slightly when properly surveyed.
Quality Assurance / Quality Control
Drilling completed on the project between 2020 and 2023 was supervised by on-site ASCU personnel who prepared core samples for assay and implemented a full QA/QC program using blanks, standards, and duplicates to monitor analytical accuracy and precision. The samples were sealed on site and shipped to Skyline Laboratories in Tucson AZ for analysis. Skyline’s sample prep, analytical methodologies, and quality control system complies with global certifications for Quality ISO9001:2008.
Technical aspects of this news release have been reviewed and verified by Allan Schappert – CPG #11758, who is a qualified person as defined by National Instrument 43-101– Standards of Disclosure for Mineral Projects.
Links from the Press Release
Figures 1-8: https://arizonasonoran.com/projects/cactus-mine-project/press-release-images/
February 21, 2024: https://arizonasonoran.com/news-releases/arizona-sonoran-announces-a-positive-pre-feasibility-study-for-the-cactus-mine-project-with-a-us-509m-post-tax-npv-and-55-kstpa/
January 30, 2024: https://arizonasonoran.com/news-releases/arizona-sonoran-announces-2024-work-plan/
January 10, 2024: https://arizonasonoran.com/news-releases/arizona-sonoran-extends-mineralization-674-ft-205-m-below-cactus-west-mineral-resource-shell-drills-731-ft-223-m-of-0.92-cut-of/
Neither the TSX nor the regulating authority has approved or disproved the information contained in this press release.
About Arizona Sonoran Copper Company (www.arizonasonoran.com | www.cactusmine.com)
ASCU’s objective is to become a mid-tier copper producer with low operating costs and to develop the Cactus and Parks/Salyer Projects that could generate robust returns for investors and provide a long term sustainable and responsible operation for the community and all stakeholders. The Company’s principal asset is a 100% interest in the Cactus Project (former ASARCO, Sacaton mine) which is situated on private land in an infrastructure-rich area of Arizona. Contiguous to the Cactus Project is the Company’s 100%-owned Parks/Salyer deposit that could allow for a phased expansion of the Cactus Mine once it becomes a producing asset. The Company is led by an executive management team and Board which have a long-standing track record of successful project delivery in North America complemented by global capital markets expertise.
For more information
Alison Dwoskin, Director, Investor Relations
647-233-4348
adwoskin@arizonasonoran.com
George Ogilvie, President, CEO and Director
416-723-0458
gogilvie@arizonasonoran.com
Forward-Looking Statements
Forward-looking statements involve known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors which may cause the actual results, performance or achievements of ASCU to be materially different from any future results, performance or achievements expressed or implied by the forward-looking statements. Factors that could affect the outcome include, among others: future prices and the supply of metals; the results of drilling; inability to raise the money necessary to incur the expenditures required to retain and advance the properties; environmental liabilities (known and unknown); general business, economic, competitive, political and social uncertainties; results of exploration programs; accidents, labour disputes and other risks of the mining industry; political instability, terrorism, insurrection or war; or delays in obtaining governmental approvals, projected cash operating costs, failure to obtain regulatory or shareholder approvals.
Although ASCU has attempted to identify important factors that could cause actual actions, events or results to differ materially from those described in forward-looking statements, there may be other factors that cause actions, events or results to differ from those anticipated, estimated or intended. Forward-looking statements contained herein are made as of the date of this news release and ASCU disclaims any obligation to update any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or results or otherwise, except as required by applicable securities laws.
“News stories of hurricanes and wildfires, droughts and floods are everywhere. It’s easy to feel paralyzed or give up.” Despite the headlines, Cecilia Perla is optimistic. “We need to pay attention to the problem, but also direct our efforts into action rather than despair.”
She’s spent over a decade reshaping copper analysis and decarbonization, and contributing her expertise to governments, universities and NGOs worldwide. And as the United Nations recognizes World Environment Day this June, there’s no better time than now to be enthusiastic about the future of ecosystem restoration.

U.N. Sustainable Development Goals (SDG) Applied to Copper Mining
Perla, the Sustainability VP for Nuton Technologies, sees good things ahead. “We need to double down on humanity’s capacity to change, our creativity and what Hannah Ritchie calls ‘pragmatic optimism’,” she says referring to sustainability data scientist, researcher and author of the 2024 book, Not the End of the World: How Can We Be the First Generation to Build a Sustainable Planet. Recognized by Bill Gates as “eye-opening and essential,” Ritchie’s book points to progress made in lowering carbon emissions, deforestation and air quality. “She’s a glass-half-full type of person, just like me.”
Though for Nuton this is a year-round effort, the U.N.’s World Environment Day in June provides an opportunity to showcase how the mining industry — historically associated with environmental degradation — can become a key innovator for ecosystem restoration.
Nuton’s heap leaching technology, in particular, is a source of great hope in the efforts to find new ways to produce copper with a lower environmental footprint. Nuton embraces a ground-up-to-global mindset for copper extraction driven by a company ethos of sustainability and alignment with the United Nations’ sustainable development goals.
“We must have a vision of what the post-mining land use for the site is and how we get there,” says Perla referring to Nuton’s ambition to accelerate opportunities for land restoration, one of the five pillars of Positive Impact Strategy. “In the big scheme of things, mining is a temporary land use. We should keep an open mind about what it can become once mining concludes.”
Along with land, Nuton’s Positive Impact Strategy encompasses four additional pillars—water, energy, materials, and society. “This year, we are seeing Nuton germinate, having announced the first industrial-scale deployment of our technology at the Johnson Camp Mine, owned and operated by our partner Excelsior Mining,” Perla says. “We will have more exciting news to share as we mature as a venture and show our partners and the market the full value of Nuton technologies.”
The World Environment Day 2024 Motto: #GenerationRestoration
This year’s World Environment Day focuses on land restoration, desertification and drought resilience under the slogan, “Our land. Our future. We are #GenerationRestoration.”
The United Nations sponsors World Environment Day to encourage worldwide awareness and action to protect our environment.
Since 1973, World Environment Day has been the largest global platform for environmental public outreach. Its mission reads, “To keep global warming below 1.5°C [34.7°F] this century, we must cut annual greenhouse gas emissions in half by 2030. Without action, exposure to air pollution beyond safe guidelines will increase by 50 percent within the decade, and plastic waste flowing into aquatic ecosystems will nearly triple by 2040.”

The Future of Sustainable Copper Mining Is Gaining Traction
Nuton is right in line with #GenerationRestoration, this year’s motto for World Environment Day. According to Perla, “Nuton is built on this spirit. Here’s a new technology unlocking opportunities to meet copper demand with a much lighter footprint and less stress on our planet than conventional copper processing technologies.”
As for the future of sustainable copper mining? It´s on its way. Here’s how Nuton’s heap leaching technology already alleviates environmental impact and increases profits.
Lighter Environmental Impact to Meet Copper Demand
It’s simple, according to Perla. “Nuton exists because we need to produce more copper, but we need to do it more sustainably. We focus not only in the what, but also on the how copper is produced.”
“The vast majority of copper comes from primary sulfides, which traditionally go through a process of concentration, smelting and refining,” she says. “Nuton technologies provide an alternative to leaching copper sulfide ores with the help of our carefully cultivated bacteria and unique catalysts and reagents.”
Stronger Economic Impact for Sustainable Copper Mining
Nuton’s ambition to produce copper with a lower carbon footprint, while conserving water, energy, and costs, aligns with the goals of World Environment Day.
World Environment Day 2024 is just one day this summer. But thanks to Perla and the Nuton team, ecosystem restoration and conservation is an everyday ambition.

Excelsior Mining Corp. (TSX: MIN) (OTCQB: EXMGF) (FSE: 3XS) (“Excelsior” or the “Company”) is pleased to announce that it has received the US$5 million infrastructure access payment from Nuton LLC (“Nuton”), a Rio Tinto venture. This payment was provided as a result of Nuton electing to proceed to Stage 2 of the existing Option Agreement (the “Agreement”) (see Excelsior press release dated May 15, 2024). The purpose of the Agreement is for Nuton to evaluate the use of its Nuton™ copper heap leaching technologies at Excelsior’s Johnson Camp mine in Cochise County, Arizona. Under the Agreement, Excelsior remains the operator and Nuton funds Excelsior’s costs associated with a two-stage work program at Johnson Camp.
As Nuton has elected to proceed to Stage 2, it made the US$5 million payment to Excelsior for the use of existing infrastructure at the Johnson Camp mine for the Stage 2 work program. Nuton will also be responsible for funding all of Excelsior’s costs associated with Stage 2. The full Stage 2 work program is anticipated to take up to five years, and, if successful, will demonstrate key elements of the Nuton technologies at industrial scale. It will proceed based on milestones related to engineering and mobilization, infrastructure and construction, mining, leaching, copper production and post-leach rinsing. Mining is expected to commence in year one with first copper produced from technology in 2025.
The completion of all milestones would result in full scale commercial production of Nuton copper over several years at Johnson Camp. Revenue from operations will first be used to pay back Stage 2 costs to Nuton and will then be credited to Excelsior’s account after fulfillment of Excelsior’s applicable royalty and stream obligations.
Rio Tinto has developed the NutonTM technologies, an extensive portfolio of advanced copper heap leaching technologies targeted at primary sulfide minerals (including lower grade mineral deposits), which could not otherwise be processed economically using traditional leaching or sulfide processing technologies. These technologies offer the potential to produce additional copper from new and ongoing operations in a cost-effective manner that has significant environmental benefits when compared with traditional primary sulfide processing technologies.
Webinar
Stephen Twyerould President & CEO, and Robert Winton SVP & General Manager, will be presenting a live-video webinar with Q&A on 29, May 2024 at 4:00pm (EDT) to go over the recently announced Nuton Stage 2 Option Agreement. The event will be hosted by Amvest Capital. Those wishing to participate in the video-webinar can do so by Registering Here.
About Nuton
Nuton is an innovative venture that aims to help grow Rio Tinto’s copper business. At the core of Nuton is a portfolio of proprietary copper leaching related technologies and capability – a product of almost 30 years of research and development. Nuton offers the potential to economically unlock copper from primary sulfide resources through leaching, achieving market-leading recovery rates and contributing to an increase in copper production at new and ongoing operations. One of the key differentiators of Nuton is the ambition to produce the world’s lowest footprint copper while having at least one Positive Impact at each of our deployment sites, across our five pillars: water, energy, land, materials and society.
About Excelsior Mining
Excelsior “The Copper Solution Company” is a mineral exploration and production company that owns and operates the Gunnison Copper Project in Cochise County, Arizona. The project is a low cost, environmentally friendly in-situ recovery copper extraction project that is permitted to 125 million pounds per year of copper cathode production. Excelsior also owns the past producing Johnson Camp Mine and a portfolio of exploration projects, including the Peabody Sill and the Strong and Harris deposits.
For more information on Excelsior, please visit our website at www.excelsiormining.com.
For further information regarding this press release, please contact:
Excelsior Mining Corp.
Concord Place, Suite 300, 2999 North 44th Street, Phoenix, AZ, 85018.
Shawn Westcott
T: 604.365.6681
E: info@excelsiormining.com
www.excelsiormining.com
Cautionary Note Regarding Forward-Looking Information
This news release contains “forward-looking information” concerning anticipated developments and events that may occur in the future. Forward looking information contained in this news release includes, but is not limited to, statements with respect to: (i) the potential of well stimulation to improve performance of the Company’s mineral projects; (ii) the intention to deploy the Nuton® technology at the Johnson Camp mine and future production therefrom; (iii) the details and expected results of the stage two work program; and (iv) future production and production capacity from the Company’s mineral projects.
In certain cases, forward-looking information can be identified by the use of words such as “plans”, “expects” or “does not expect”, “budget”, “scheduled”, “estimates”, “forecasts”, “intends”, “anticipates” or “does not anticipate”, or “believes”, or variations of such words and phrases or state that certain actions, events or results “may”, “could”, “would”, “might”, “occur” or “be achieved” suggesting future outcomes, or other expectations, beliefs, plans, objectives, assumptions, intentions or statements about future events or performance. Forward-looking information contained in this news release is based on certain factors and assumptions regarding, among other things, the amended permit will not be appealed, work plans will be approved in a timely manner, the availability of financing to continue as a going concern and implement the Company’s operational plans, the estimation of mineral resources and mineral reserves, the realization of resource and reserve estimates, expectations and anticipated impact of the COVID-19 outbreak, copper and other metal prices, the timing and amount of future development expenditures, the estimation of initial and sustaining capital requirements, the estimation of labour and operating costs (including the price of acid), the availability of labour, material and acid supply, receipt of and compliance with necessary regulatory approvals and permits, the estimation of insurance coverage, and assumptions with respect to currency fluctuations, environmental risks, title disputes or claims, and other similar matters. While the Company considers these assumptions to be reasonable based on information currently available to it, they may prove to be incorrect.
Forward looking information involves known and unknown risks, uncertainties and other factors which may cause the actual results, performance or achievements of the Company to be materially different from any future results, performance or achievements expressed or implied by the forward-looking information. Such factors include risks related to the Company not obtaining adequate financing to continue operations, the breach of debt convenants, risks inherent in the construction and operation of mineral deposits, including risks relating to changes in project parameters as plans continue to be redefined including the possibility that mining operations may not be sustained at the Gunnison Copper Project, risks related to the delay in approval of work plans, variations in mineral resources and reserves, grade or recovery rates, risks relating to the ability to access infrastructure, risks relating to changes in copper and other commodity prices and the worldwide demand for and supply of copper and related products, risks related to increased competition in the market for copper and related products, risks related to current global financial conditions, risks related to current global financial conditions and the impact of any resurgence of COVID-19 on the Company’s business, uncertainties inherent in the estimation of mineral resources, access and supply risks, risks related to the ability to access acid supply on commercially reasonable terms, reliance on key personnel, operational risks inherent in the conduct of mining activities, including the risk of accidents, labour disputes, increases in capital and operating costs and the risk of delays or increased costs that might be encountered during the construction or mining process, regulatory risks including the risk that permits may not be obtained in a timely fashion or at all, financing, capitalization and liquidity risks, risks related to disputes concerning property titles and interests, environmental risks and the additional risks identified in the “Risk Factors” section of the Company’s reports and filings with applicable Canadian securities regulators.
Although the Company has attempted to identify important factors that could cause actual actions, events or results to differ materially from those described in forward-looking information, there may be other factors that cause actions, events or results not to be as anticipated, estimated or intended. Accordingly, readers should not place undue reliance on forward-looking information. The forward-looking information is made as of the date of this news release. Except as required by applicable securities laws, the Company does not undertake any obligation to publicly update or revise any forward-looking information.
Thirty minutes north of Melbourne, the second largest city in the Land Down Under, sits the Bundoora Technical Development Centre, the center of innovation for Nuton’s groundbreaking technology.
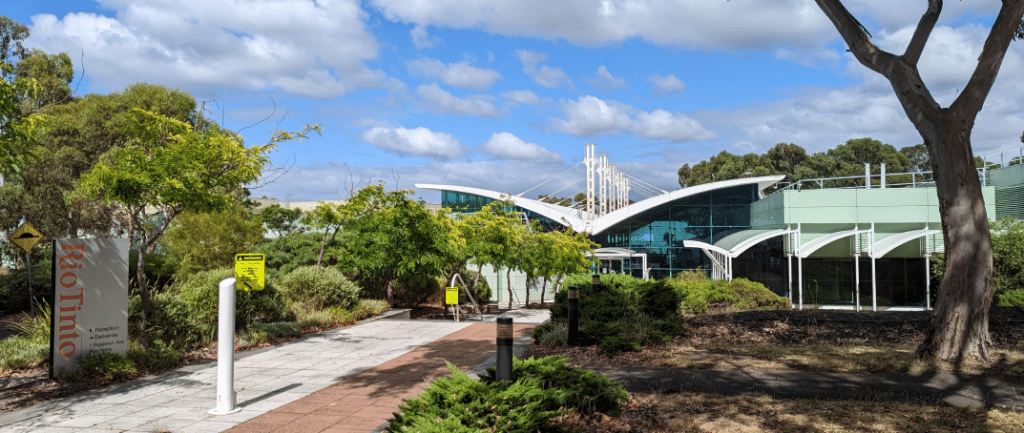

Surrounded by a lush gathering of trees and close enough to the Australian coast to feel a slight ocean breeze, the Technical Development Centre, known simply as Bundoora by Nuton and Rio Tinto teammates, is located in a beautiful spot.
“People drive through the gate in the morning, and they can’t help but be relaxed and inspired,” says Jared Osborne, General Manager of Technical Development at Rio Tinto. “Kangaroos are hopping around, the occasional big rabbit, some foxes. It’s really quite something.”
Jared says he feels even more energized when he sees the world of immense growth and possibility happening inside Bundoora.
Teams of dedicated scientists, like Jared, have already come so far and achieved so much in nearly 30 years of research and innovation at Bundoora. Back in the early 1990s, Rio Tinto executives at our Kennecott operations in Utah were looking for a solution that could minimize the amount of wasted ore bodies that were unsuitable for traditional processing. The waste was burdensome, economically unviable, and importantly—with notable implications on the environment.
In 1996, a small group of scientists working at Bundoora took a huge leap forward, finding a copper leaching technology that could extract premium quality copper with less water usage and a much smaller carbon footprint. That solution is at the heart of our new Rio Tinto venture, Nuton.
“This was a major breakthrough for a metal that we absolutely need as part of the energy transition. Copper is so vital to it,” says Jared, who joined Bundoora in 1997. “We can make a significant impact on global emissions and the legacy we leave behind with a nature-based solution.”

Over the years, technology and innovation milestones have stacked up at Bundoora. From those first tests in 1996 to small and large column tests in 2006 to a pilot plant in 2012, Bundoora teammates have seen the Nuton technology evolve and ramp up significantly.
Next is to deploy this technology on a large scale, where it can truly create a positive impact on the world. It’ll be an exciting challenge, made possible by the team at Bundoora comprised of some of the brightest minds in the field.
With a diverse team of experts from all over the world, celebrating each other’s culture and championing inclusion are major aspects of the magic at Bundoora. It’s common for teammates to bring in traditional food from their homeland to share with everyone at lunch and for all to truly get to know each other on a personal level.
Those kinds of things are organic and frequent at Bundoora.
“We’ve recruited the best in the world for over 30 years and we’ve ended up with a magnificent mix of people,” says Jared. “It really does feel like a family.”

Casa Grande, AZ and Toronto, ON, February 21, 2024 – Arizona Sonoran Copper Company Inc. (TSX:ASCU | OTCQX:ASCUF) (“ASCU” or the “Company”) today announced it has completed its NI 43-101 Prefeasibility Study (“PFS”) for its Cactus Project in Arizona, USA. The Standalone PFS outlines a lower risk, top 10 potential copper operation in the domestic USA, producing LME Grade A copper cathodes onsite via heap leach and a Solvent Extraction/Electrowinning (“SXEW”) plant. All dollar amounts referenced herein in US dollars, and all references to tons are short tons, unless otherwise noted.
The Company intends to file a technical report (the “Technical Report”) in respect of the PFS in accordance with National Instrument 43-101 – Standards of Disclosure for Mineral Projects (“NI 43-101”) on SEDAR+ (www.sedarplus.ca) under the Company’s issuer profile and the Company’s website within 45 days of the date of this news release.
A webinar will be held on February 22, 2024, at 10:00 am ET. Please join George Ogilvie, Nick Nikolakakis, Bernie Loyer and Anthony Bottrill in discussion of the PFS and the Company’s next steps by registering here https://www.bigmarker.com/vid-conferences/ASCU-VID-THF.
Cactus PFS Highlights
Scalable, Long-Life Operations
- Average annual production of approximately 55 ktons or 110 million pounds (“lbs”) of copper (“Cu”), with a peak of 74 ktons or 149 million pounds of copper
- Initial Life of Mine (“LOM”) 21 years, recovering 1,153 ktons or 2.31 billion pounds of Copper LME Grade A cathode onsite via heap leach facility and SXEW
- Maiden Proven & Probable (“P&P”) Reserves of 276.3 million tons at 0.48% Soluble Copper (“Cu TSol”) or 3.0 Billion lbs Copper
- Favourable metallurgy with a range of 85%-92% LOM average soluble copper recoveries
- Private land ownership with streamlined permitting process
- Low carbon footprint mining project:
- Powered by an existing 69 KV Transmission line with access to “Green Energy” through the Palo Verde Nuclear Plant West of Phoenix for costs of $0.07/kWh
- Heap Leach and SXEW Process
- Conveyors and radial stackers used to move ore to leach pads
Robust Economics
- First quartile capital intensity of $10,343/tonne of average annual production
- Total initial capital cost of $515 million, including $75 million of contingencies over an 18-24 month construction period
- Total revenues of $9.0 billion over 21 years
- Post-tax unlevered Free Cash Flow of $2.4 billion
- C1 Cash Costs of $1.84/lb and All in Sustaining Cost (“AISC”) of $2.34/lb
- Post-tax net present value (“NPV”) $509 million (CA$687 million) using an 8% discount rate and an internal rate of return (“IRR”) of 15.3% and using a $3.90/lb flat long-term copper price
- Pre-tax NPV $733 million (CA$990 million)
- Post-tax payback period of 6.8 years from initial production
- At $4.25/lb Copper the NPV increases to $780 million post-tax (CA$1,054 million) and $1,064 million pre-tax (CA$1,436 million), using an 8% discount rate
Significant Copper Project in the USA
- Proven & Probable (“P&P”) Reserves of 276.3 million tons at 0.48% Soluble Copper (“Cu TSol”) or 3.0 Billion lbs Copper
- Underground Proven Reserve grade of 0.89% and 0.82% Cu TSol from Cactus East and Parks/Salyer, respectively
- Measured & Indicated Resources of 5.2 billion lbs Copper and Inferred Resources of 2.2 billion lbs Copper (as announced October 16, 2023) (inclusive of reserves)
Future Opportunities to Further Improve Business Case
- Drilling to upgrade known inferred resources and bring them into the mine plan potentially increasing the LOM production, reducing underground development costs, operating expenses, capital expenses and overall strip ratio
- Drilling to prove a maiden resource at MainSpring as a potential open pit providing operational flexibility and gaining lower cost access to the Parks/Salyer deposit. Bringing MainSpring into the mine plan potentially improves operational and financial synergies within the Cactus Project
- Continued exploration success on the Cactus Project in the “Gap Zone”, below the envelope of the existing Cactus West Open Pit Shell and in the North-East Extension.
- Nuton LLC’s (“Nuton”) leaching technology driving primary sulphide optionality, currently excluded from the mine plan
George Ogilvie, ASCU President and CEO commented, “The 55,000-ton Copper Cathode per annum mine plan presented in the PFS illustrates an achievable long-life operation with robust economics and an opportunity for continued scaling of the asset. Our operation has the potential to be among the top 10 copper operations within the US, supplying the domestic supply chain with copper cathodes in the near term. With global copper mine disruptions occurring and a structural deficit currently underway, our timing to develop the asset has a high likelihood to coincide with much higher copper incentive prices. As compared to the original PEA, the PFS demonstrates a significant increase of free cash flow at a conservative long-term copper price assumption of $3.90 per pound.”
He continued, “A real organic growth opportunity exists within our 5,370 acres at the MainSpring Property. Based on initial drilling of our MainSpring property there are early indications for Mainspring to be the southern near surface extension of our Parks/Salyer deposit and thus will be a focus of drilling in 2024. Through our 2024 drilling programs, our team has the potential to convert the 1.3 billion pounds of leachable inferred resources of copper to the indicated resources category, contributing to an extended mine life. Over and above, ASCU also looks forward to the continued metallurgical testing and incorporation of the Nuton technology to our Cactus flowsheet, which if executed, lowers our cost of capital, provides a funding partner for the initial capex and ongoing operating costs, as well as provides execution support from a top global mining partner.”
“With this cornerstone now placed, we are excited to continue building Cactus, which today is a significant asset, with plenty of future optionality to continue upgrading the asset with scale.”
Bernie Loyer, ASCU SVP Projects notes “Our Cactus Project PFS demonstrates a solid business case, and the potential to deliver a long-life operation utilizing a well-established and industry proven process technology in the treatment of ore from four separate and well understood feed sources. All situated on privately held ground, this brownfield project site located within 45 minutes of the Phoenix city center which is the 10th largest metropolitan area within the United States, is wrapped with an enviable complement of all required infrastructure. Add to all of that, a project team with a strong combination of project and operational experience on complex mining projects throughout North and South America, and the foundation for the Cactus Project and future operation is well-placed.”
Pre-Feasibility Summary
The 2024 PFS outlines a lower risk and long-life copper project with low first quartile capital intensity. The heap leach operation will produce on average 55 kstpa of LME Grade A copper cathodes via SXEW. Key metrics are shown in TABLE 1 below.
Conventional open pit mining methods have been selected for the extraction of oxide and secondary sulphide material from the lower grade Cactus West pit, while the higher-grade Parks/Salyer and Cactus East deposits will be mined via underground using the Sublevel Caving (“SLC”) method from the 1,500 ft (457 m) and 1,200 ft (366 m) levels, respectively. Reserve grades of the Parks/Salyer and Cactus East deposits are high grade, at 0.93% CuT and 0.95% CuT, and 0.82% Cu TSol and 0.89% Cu TSol, respectively. The Stockpile will be a rehandling exercise moving low grade tonnage to a lined pad for leaching. Onsite facilities at the mine site will consist of an open pit, underground mining operations, a fine crushing plant incorporating all crushing, classification, agglomeration and conveying systems and an SXEW process plant. On site supporting infrastructure will include site power distribution, access roads and heap leach facilities.
Table 1: 2024 PFS Highlights 
FIGURE 1: Annual Revenues and EBITDA Over Annual Production

TABLE 2: Pre- and Post-Tax Sensitivity to the Copper Price

1 Payback period calculated starting from start of commercial production
Project Overview
The Cactus Mine Project is a brownfield project located approximately 6 mi (10 km) northwest of the city of Casa Grande and 40 road miles south-southwest of the Greater Phoenix metropolitan area in Arizona. The Cactus Mine Project is accessible on North Bianco Road off of West Maricopa-Casa Grande Highway with direct access to interstate highway 10. During historic ASARCO operations (1974-1984), a rail spur was connected directly with the United Pacific Railroad to ship concentrates to its El Paso refinery in Texas; while the spur has been removed, the onsite rail line is still in existence. Current onsite infrastructure includes power lines and substation, water wells and a water pond, geological buildings, core sheds and administrative offices, keeping the capital intensity low and demonstrating robust economics.
Since 2019, ASCU has drilled 141 new holes at the Cactus West and East deposits to support verification, metallurgical testing, and resource extension for the Cactus mineral resource estimate. The Parks/Salyer resource database is composed primarily of 74 new holes drilled by ASCU between late 2020 and 2023. The historical ASARCO holes for the district comprised of 171 drillholes. The bulk of these holes were in the Cactus West and Cactus East deposits or comprised regional exploration holes. An extensive verification and re-assay programs were undertaken to support the use of historical drilling in resource estimates. Since 2020, ASCU has drilled 514 sonic drillholes to support resource estimates on the stockpile. In addition to verification of historical drilling, for all ASCU holes physical checks on collar, downhole survey, logging, and assay quality assurance and quality control (“QA/QC”) have been completed by the qualified person.
The Cactus Mine Project is host to a large porphyry copper system that has been dismembered and displaced by Tertiary extensional faulting. The major host rocks are Precambrian Oracle Granite and Laramide monzonite porphyry and quartz monzonite porphyry. The mine trend features the formation of horst and graben blocks of mineralization where the Cactus deposits are situated, extending from the Cactus East deposit, southwest to the Parks/Salyer deposit. Drilling to the northeast and southwest along the trend indicates that mineralization continues in both directions and at depth at the Cactus West deposit.
FIGURE 2: Cactus 2024 PFS Production Profile: Mined Tons and Recovered Copper

Reserves and Resources
The PFS is based on the updated 2023 Mineral Resource Estimate (“MRE”), as published on October 16, 2023, showing a 221% increase of leachable Measured and Indicated (“M&I”) pounds over the mineral resource base used in the 2021 PEA. The Mineral Resources and Reserves for the Cactus Mine Project are shown in TABLES 3 and 4 and illustrated in FIGURE 3 below.
FIGURE 3: Isometric View of the Copper Mineral Estimation Domains
Table 3: Cactus Project Total Measured, Indicated and Inferred Mineral Resource

Notes:
1. Leachable copper grades are reported using sequential assaying to calculate the soluble copper grade. Primary copper grades are reported as total copper, Total category grades reported as weighted average copper grades of soluble copper grades for leachable material and total copper grades for primary material. Tons are reported as short tons.
2. Stockpile resource estimates have an effective date of 1 March 2022, Cactus resource estimates have an effective date of 29th April 2022, Parks/Salyer resource estimates have an effective date of 19th May 2023. All resources use a copper price of US$3.75/lb.
3. Technical and economic parameters defining resource pit shell: mining cost US$2.43/t; G&A US$0.55/t, 10% dilution, and 44°-46° pit slope angle.
4. Technical and economic parameters defining underground resource: mining cost US$27.62/t, G&A US$0.55/t, and 5% dilution.
5. Technical and economic parameters defining processing: Oxide heap leach (HL) processing cost of US$2.24/t assuming 86.3% recoveries, enriched HL processing cost of US$2.13/t assuming 90.5% recoveries, Primary mill processing cost of US$8.50/t assuming 92% recoveries. HL selling cost of US$0.27/lb; Mill selling cost of US$0.62/lb.
6. Royalties of 3.18% and 2.5% apply to the ASCU properties and state land respectively. No royalties apply to the MainSpring (Parks/Salyer South) property.
7. For Cactus: Variable cutoff grades were reported depending on material type, potential mining method, and potential processing method. Oxide material within resource pit shell = 0.099% TSol; enriched material within resource pit shell = 0.092% TSol; primary material within resource pit shell = 0.226% CuT; oxide underground material outside resource pit shell = 0.549% TSol; enriched underground material outside resource pit shell = 0.522% TSol; primary underground material outside resource pit shell = 0.691% CuT.
8. For Parks/Salyer: Variable cut-off grades were reported depending on material type, associated potential processing method, and applicable royalties. For ASCU properties – Oxide underground material = 0.549% TSol; enriched underground material = 0.522% TSol; primary underground material = 0.691% CuT. For state land property – Oxide underground material = 0.545% TSol; enriched underground material = 0.518% TSol; primary underground material = 0.686% CuT. For MainSpring (Parks/Salyer South) properties – Oxide underground material = 0.532% TSol; enriched underground material = 0.505% TSol; primary underground material = 0.669% CuT.
9. Mineral resources, which are not mineral reserves, do not have demonstrated economic viability. The estimate of mineral resources may be materially affected by environmental, permitting, legal, title, sociopolitical, marketing, or other relevant factors.
10. The quantity and grade of reported inferred mineral resources in this estimation are uncertain in nature and there is insufficient exploration to define these inferred mineral resources as an indicated or measured mineral resource; it is uncertain if further exploration will result in upgrading them to an indicated or measured classification.
11. Totals may not add up due to rounding.
As shown in TABLE 4below, a total of 276 million short tons or 3.0 billion pounds were converted into a P&P Reserve out of the leachable M&I Resource base of 4.43 billion lbs, representing a conversion rate of 68%. The Inferred material and primary sulphides are treated as waste, with conversion drilling at Cactus West, a focus for 2024 as part of the dual track ASCU/Nuton Work Plan as announced on January 30, 2024. Mineral resources that are not mineral reserves do not have demonstrated economic viability.
Table 4: Cactus Mine Project Reserves Statement by Deposit
Notes to the Mineral Reserves:
1. Mineral Reserves have an effective date of November 10, 2023. The Qualified Person for the underground estimates of Cactus East and Parks/Salyer is Nat Burgio of AGP Mining Consultants Inc. The Qualified Person for the open pit estimates of Cactus West and Stockpile is Gordon Zurowski of AGP Mining Consultants Inc.
2. The Mineral Reserves were estimated in accordance with the CIM Definition Standards for Mineral Resources and Reserves.
3. The Mineral Reserves are supported by a combined open pit and underground mine plan, based on open pit and underground designs and schedules, guided by relevant optimization procedures.
Inputs to that process are:
• Metal prices of Cu $3.70/lb.
• Processing costs which are variable and based upon material type, processing destination, copper grade, and copper recovery. Processing costs include a fixed unit cost component, a net consumption cost, and a cost for refining and selling copper cathode.
• General and administration cost of $0.47/ton processed.
• Royalty cost of 2.5% for BCE land and 2.54% for Parks/Salyer, Cactus and Stockpile Ores, excluding BCE ore – royalty discussion noted below.
• Process recoveries which are variable depending upon mineralization type, sequential copper grades, and comminution size.
• Open pit geotechnical design criteria from Call and Nicholas, Underground geotechnical design criteria from Call and Nicholas, Open pit mining costs including an escalation factor with pit depth.
• Underground mining cost of $27.62.
4. The footprint delineations for the Cactus East and Parks/Salyer mines were based on a resource model block cash flow dollar value (CFTC1) of $27.62 (net of process, G/A and royalties). Drawpoints were shut-off when the grade value fell below a CFTC1 of $27.62 following the necessary removal of swell material within the footprint.
5. Dilution and mining loss adjustments are incorporated into the underground mining inventories by way of cave flow modelling software. Inferred resources included in the mixing process have been assigned zero grade. No allowance for mining dilution or ore loss has been provided in the open pit mining inventories.
Mining Operations
The Cactus Mine plan includes production from four separate mining areas: Cactus West Open Pit, Historical Stockpile, Cactus East Underground, and Parks/Salyer Underground. Ore processing in the mine schedules involves oxides and secondary sulphides being processed on a heap leach after multi-stage crushing.
The mine production schedule is initially focused on the surface sources of ore (Stockpile and Cactus West Open Pit) beginning in year -1, along with Parks/Salyer underground starting development in Year 1. The Cactus East deposit is developed later in the mine life, starting in Year 8. Cactus West and the Stockpile ore sources are depleted in Year 7 after which the ore stream becomes exclusively underground. The overall site layout is shown in FIGURE 8.
The Cactus West mine life consists of 2 phases and includes one year of pre-stripping and seven years of mining. Phase 1 starts with 24 million tons (“Mt”) of pre-production stripping and is completed in Year 4. Phase 2 mining begins in Year 2 and is mined out in Year 6. Target ore production is 12 Mt per annum with a peak mining rate of 47 Mt in Years 2 and 3. A total of 75.5 Mt of leach ore grading 0.307% total copper is mined at a strip ratio of 1.9 to 1. Bench elevations at Cactus West range from the 1,440-ft level to the 380-ft level.
FIGURE 4: Cactus West After Phase 1 and Phase 2
Over the course of the open pit mine schedule, approximately 13.1 Mt of low-grade ore is stockpiled and reclaimed in order to smooth the ore release from the open pits. This amount includes approximately 3.0 Mt of material stockpiled in the first three years of mining, and then processed in Year 3 and 4, and another 10 Mt stockpiled later in the mine schedule before being reclaimed in Years 7 and 8.
Historic Stockpile (FIGURE 5) mining begins near the end of the pre-production year with approximately 3.0 Mt of ore sent to the leach pad. Mining continues concurrently with the Cactus West pit into Year 7 at an annual ore production rate of 12 Mt. A total of 76.8 Mt of leach ore at 0.163% total copper is mined. A small amount, 5.5 Mt of waste is mined from the historic stockpile and sent to the waste storage areas.
Figure 5: Stockpile Mining

The initial Parks/Salyer SLC (FIGURE 6) level will commence at 1,120 ft (341 m) below surface and include 11 sublevels to a final depth of 1,930 ft (588 m) below surface. Access to the Parks/Salyer deposit will be via a surface portal and twin declines. One decline will be dedicated to ore haulage using an inclined conveyor and the other decline providing access for personnel and equipment. Production extends from year 1 to 20, with steady state production beginning in year 7 to year 20, peaking at 6.9 Mtpa in year 13. A total of 96 Mt of leach ore @ 0.82% Cu TSol will be processed.

The initial Cactus East SLC (FIGURE 7) level will commence in year 9 at 1,325 ft (404 m) below the surface and will be comprised of 7 sublevels to a final depth 1,845 ft (562 m) below surface. Access will be via a single decline with a portal located within the existing Cactus West pit. Ore haulage to surface will be via a vertical conveyor which can be supplemented with truck haulage to surface via the open pit if necessary. Production is planned from year 9 to 19, with steady state production beginning in year 12, peaking at 3.9 Mtpa in year 15. A total of 28 Mt of leach ore @ 0.89% Cu TSol will be processed.

SLC production crosscuts have primarily been designed so that each level is horizontally offset from the level above and below. The design parameters for the SLC production drives at Cactus East and Parks/Salyer are in line with other SLC operations.
The amount of ore to be extracted will be limited in the upper three production levels to the following proportions:
• First Level ~40% (swell only)
• Second Level ~60%
• Third level ~100%
• Lower levels >100% to shutoff grades or dollar values.
The production strategy will help control caveability, minimise the formation of air gaps and create a blasted ore blanket above the production levels to minimise early dilution entry from the overburden rocks. These restricted draw rates also apply to areas where large step-outs distances are required from one sublevel to the next.
The Cactus East Ore/Waste Handling System consists of a crusher station and a 1,600 ft (488 m) vertical conveyor with a capacity of 630 tons/h that will convey ore from the top of the orebody to surface via a vertical raise feeding an overland conveyor. Ore will be hauled by 55-ton diesel trucks to a sizer located adjacent to the bottom of the vertical conveyor. Ore will be crushed to a maximum 6-in dimension. A short conveyor from the sizer will feed the vertical conveyor. Waste will be trucked to the portal for disposal within the Cactus West open pit.
The mine plan for Parks/Salyer consists of two ramps with one dedicated for material handling. The ore/waste handling system consists of a series of initially four, extending to five switchback conveyors and two crushing sizers on -270 L, one of which will subsequently be relocated at the -470 L. that will deliver material from the mine working levels to the surface portal, from where materials will then be transported on surface via an overland conveyor.
Ventilation is driven by a fresh air drive developed from the access drive, in which the fresh air will be splitting right and left to connect to the return air drives at the extremities of the footprint. This allows natural flow of ventilation through the entire footprint.
Figure 8: Overall Site Layout
Processing Operations
Material mined from the existing stockpile will be placed in 20-ft lifts and material from all other sources will be stacked in 30-ft lifts. Material will be reclaimed and transferred by haul truck to the crushing circuit where it will be crushed down to P80 minus ¾-in. From the crushing circuit, the material will transfer by overland conveyor to the agglomeration drums, mobile transfer conveyors, and mobile radial stacker to be placed on the geomembrane lined heap leach facility (HLF).
Leaching solutions, containing dilute sulfuric acid will be pumped and applied to the top of each lift and allowed to percolate though the copper leach material. Copper is dissolved into the solution while acid is consumed at approximately 13.6 lb/ton of material leached. Acid consumption is net of regenerated acid in the SXEW process. The height of the leach material on the pad will eventually reach approximately 180 ft (55 m) in overall height.
The pregnant leach solution (PLS) collected from the HLF will be conveyed in pipes to the heap leach ponds where it will be pumped for processing in a copper SX/EW plant capable of producing initially up to 30,000 ton/y of copper cathodes with a design PLS flow of up to 12,000 gpm and grade at approximately 3.0 g/pL Cu based on an overall 71% total copper (85-92% soluble copper) recovery from the heap leaching method for the resources considered. The solvent extraction plant is designed to be operated in a series, parallel, or series-parallel configurations with a single stage of stripping. The optionality of the solvent extraction plant will allow the plant to operate at 4,000 gpm, 8,000 gpm, or 12,000 gpm PLS flowrates based on the variability in copper grades and tonnages in the mine plan.
The electrowinning circuit capacity will be expanded in Year 3, doubling in size to the overall plant capacity required to a nominal 60,000 ton/y of copper cathodes.
The principal objective of the HLF design is to efficiently extract copper by leaching metals within the geotechnically stable facility. The anticipated ore production will be approximately 65,000 tons/d for the first seven years and reduced to 24,500 tons/d after that for the life-of-mine (LOM) for an average of 55,000 tons of cathode production annually. The pad will be loaded with conveyor belts coming in from the west along the northern side of the pad to discharge to the eastern area of the pad (Phase 1). This area provides a relatively flat area that facilitates the construction of the first phase of the pad and allows for mining of the existing stockpile to liberate additional space for the consecutive phases of construction. A visual representation of the flow sheet is depicted below, in FIGURE 9.
FIGURE 9: Process Flowsheet (Conceptual Flow Diagram)

Cost Estimates
The capital cost estimates for the PFS were developed with a -15% to +20% accuracy and an estimated contingency of approximately 15% according to the Association of the Advancement of Cost Engineering International Class 4 estimate requirements. The estimates include the cost to complete the design, engineering, procurement, construction and commissioning of all process plant facilities.
The project capital cost estimate was compiled by Ausenco Engineering USA South Inc. (“Ausenco”) with input from AGP and Samuel Engineering for the open pit, underground mining operation, SXEW process plant, conveying, crushing and screening equipment, site sub-station, site power distribution, access roads, heap leach facilities and associated infrastructure. all direct costs, growth allowances, project indirect costs, and associated contingency within their scope of work, but separately identified.
An 18–24-month construction period is projected with the initial capital costs and sustaining development costs summarized in the table below.
Table 5: Initial and Sustaining Capital Costs (18% LOM contingency included)

Operating Cost Summary
Mining operating cost estimates, prepared by AGP, are based on a small owner’s team managing mining activities using an owner-operator model. Process operating cost estimates were prepared by Samuel Engineering and G&A cost estimates were prepared by Ausenco with input from ASCU, as summarized in the table above.
Unit Cost table
Operating costs have been based on a delivered diesel price of $3.49 per gallon and are in line with current local pricing. Power will be sourced from a grid supplying 69kv to site, with power costs estimated at $0.07/kWh.
Site Infrastructure Summary
The facilities at the mine site will consist of an open pit, underground mining operation, SXEW process plant, conveying, crushing and screening equipment, site sub-station, site power distribution, access roads, heap leach facilities and associated infrastructure.
Local Resources and Infrastructure
The Cactus Mine Project is located approximately 3 miles northwest of the City of Casa Grande, Pinal County, Arizona. It is 40 road miles south-southeast of the Greater Phoenix metropolitan area and approximately 70 road miles northwest of Tucson. It is easily accessible from the Interstate 10 (I-10) freeway, which is approximately 10 mi east of the historic Sacaton Mine. The Greater Phoenix area is a major population centre (approximately 4.8M persons) with a major airport and transportation hub and well-developed infrastructure and services that support the mining industry. Location benefits include:
• Electric power is available from Arizona Public Service’s (APS) 69 kV transmission line which passes on the South side of the site and connects to an existing substation owned by ASCU.
• Paved road and easy access to the interstate networks for transport and two major Interstates Highways (I-10 & I-8) less than 10 miles away from the Cactus Mine Project.
• Well established road network existing from either ADOT, Pinal County or the City of Casa Grande surrounding the property.
• Union Pacific rail road line and rail spur adjacent to the property.
• Five miles distance to Casa Grande and allowing the ability of the town to supply materials/consumables in addition to just labor.
• Kinder Morgan/El Paso Natural Gas two high pressure natural gas pipelines adjacent to the property should natural gas be needed.
• The City of Casa Grande Water Treatment Facility located within 3 miles of the Cactus Mine Project that can supply effluent water for the operation and possibly treat waste.
• An existing Arizona Water Company potable water line is adjacent to the property.
• Water supply is already available via buried pipeline to the property boundary as a result of prior mining and commercial operations.
• The cities of Casa Grande and Maricopa are nearby and, combined with Phoenix, can supply sufficient skilled labor for the Cactus Mine Project. In addition, the State of Arizona has a significant presence of copper mining in the state that can specifically provide skilled labor to the Cactus Mine Project.
Metallurgical Testwork
The metallurgical studies and testing for the Cactus Project has been ongoing since late 2019, via 45 column tests covering the resources identified in the study. Additional tests include, bottle roll testing, mineralogical analyses and other metallurgical and materials property testing. Arizona Sonoran geologists are working with metallurgical engineers to quantify the metallurgical performance from the samples obtained in a large drilling campaign. The drill core samples were safely recovered and placed in bags to be studied by geologists and subsequently shipped for testing to a well-established Mineral Processing research and development firm in Reno, Nevada (McClelland Analytical Service Laboratory (“McClelland”), an ISO 9000, ISO 17025 accredited facility). Additional testing work was completed on-site by ASCU staff and at HydroGeoSense Inc. (“HGS”) laboratories in Tucson, Arizona. The metallurgical test program completed at McClelland has been developed by and supervised by Mr. James L. Sorensen. Mr. Sorensen has also reviewed and inspected the ongoing metallurgical testing at site and information developed by HGS.
Ownership, Social License, Permitting, Taxes and Royalties
The Cactus Mine Project is 100% controlled by ASCU through its wholly owned subsidiary Cactus 110 LLC and encompasses an area of approximately 5,381 acres, as shown in FIGURE 10. The Cactus Mine Project includes exploration and mining on private land and on two Arizona State Land Department (“ASLD”) leases. There is no federal nexus for permitting the project.
Of the 5,381 acres, 4,731.92 acres is fee simple land, three ASLD prospecting permits that the State has surface and minerals (649.12 acres), two ASLD prospecting permits that the State has minerals only with ASCU owning the surface (797.5 acres) and 18 BLM unpatented mining claims, this is for mineral only as ASCU owns the surface rights (320 acres). The BLM unpatented mining claims are outside of the known mineralization and there are currently no plans for mining at this area.
FIGURE 10: Cactus Land Ownership Map
ASCU has a well-developed community engagement plan that it has implemented through numerous public meetings and outreach. With the presence of legacy mining in the Casa Grande area and the determination of Cactus as a “brownfield” and disturbed site, the local community is supportive of the Cactus Mine Project. There is no significant opposition to the Cactus and Parks/Salyer Project.
Permitting is limited to State of Arizona-required permits including the Aquifer Protection Permit, Industrial Air permits and the Mined Land Reclamation Permit which ASCU has received from state regulators. Modifications of each will be required to address changes in the mine plan presented in this PFS.
A Mined Land Reclamation Plan was completed and submitted to the Arizona State Mine Inspector’s office in January 2023. The submitted plan does not include the Parks/Salyer mine plan and will therefore need to be modified to reflect the addition of new facilities described in this PFS.
In 2009, approximately 25 years after the Cactus Mine ceased operation, the mine was conveyed to the ASARCO Multi-State Environmental Custodial Trust as part of ASARCO bankruptcy proceedings, who helped lead a subsequent remediation program. Structures were demolished and reclaimed, and site characterization studies were conducted. Based on the results of the characterization studies and reclamation work, the ADEQ released ASCU from potential legacy liabilities, under the terms of the Prospective Purchaser Agreement (“PPA”) signed in 2019. The PPA does not cover unidentified environmental conditions or contamination.
A corporate tax rate of 25.9% combined federal and state taxes has been applied to taxable income in the PFS with an effective tax rate of 22.3% after applicable deductions and credits. A royalty of 2.5% was applied to all sales from the Cactus deposits and the Parks/Salyer deposit. A royalty of 2.5% was applied to all sales from the Bronco Creek Exploration (“BCE”) land (west of the Parks/Salyer deposit). As cathodes will be produced onsite, no transport or refining fees have been added.
The Cactus Mine Project is subject to three royalties based on potential mining production. Tembo/Elemental Altus holds a 3.18% net smelter return (“NSR”) royalty, with an option to buy back 0.64% possible for payment of $8.9 million. BCE holds a 1.50% NSR royalty based on a portion of the Parks/Salyer Deposit, with an option to buy back 1% for payment of $0.5 million. ASLD owns a sliding net return royalty (2.00% to 8.00% and estimated at 2%) that is payable to ASLD and the State Trust on a portion of production from the Parks/Salyer Deposit, overlapping with BCE land. ASCU still needs to formalize the royalty percentages with ASLD. Formalization will be done once ACSU submits a Mineral Development Report to ASLD to convert the existing MEP to a Mineral Lease.
Exploration Upside
The Cactus Mine Project mineral resource estimate includes three deposits along a 4 km mine trend. The mineralization is present within horst blocks developed as part of regional extensional faulting. High grade mineralization was emplaced within brecciated host granite at the margin of the intruding monzonite porphyry zone and locally forms a linear NE trend called the mine trend.
Drilling has demonstrated potential for extending mineralization south of Parks/Salyer onto MainSpring as shown in FIGURE 11. At the Cactus West deposit, potential to extend resources exists towards the SW adjacent to the PFS pit and also on the NE edge. These are zones where higher-grade primary mineralization as part of the mine trend have been intercepted previously. The NE Extension zone represents a further horst block of mineralization to the NE of Cactus East that to date has been explored by wide spaced historical drilling. ASCU drilled one exploration hole into the target in 2023. The Gap Zone represents a deeper target between Parks/Salyer and Cactus West. There is potential to explore for a down dropped extension of Parks/Salyer within this zone with analogies to Cactus East.
Figure 11: Mineral Resources and Near-Term Exploration

Next Steps
Future opportunities to build value may include a potential MainSpring starter pit, and the successful application of the Nuton technology for leaching of primary sulphides. A Preliminary Economic Assessment (“PEA”) will define the impact of those two opportunities.
• A PEA inclusive of an inferred MainSpring mineral resource and the application of the Nuton technologies to the primary sulphides using the same PFS assumptions is underway with M3 Engineering as lead consultant. The study is expected in the summer of 2024
• Continued metallurgical testing
• Infill drilling at MainSpring and around the Cactus West Pit
• An updated PFS to include the MainSpring opportunity is expected in 2H 2024
• A DFS is expected to begin post MainSpring PFS, for release in 1H 2025
• Nuton and ASCU have agreed to working towards the Integrated Nuton PFS release by the end of 2024, unless extended mutually by both parties.
• Nuton phase 2 metallurgy
• Infill drilling at MainSpring and Cactus West at depth and southwest and west of the deposit
Links from the Press Release:
Webinar: https://www.bigmarker.com/vid-conferences/ASCU-VID-THF
Figures and Tables: https://arizonasonoran.com/projects/cactus-mine-project/press-release-images/
SEDAR+: https://www.sedarplus.ca
January 30, 2024: https://arizonasonoran.com/news-releases/arizona-sonoran-announces-2024-work-plan/
October 16, 2023: https://arizonasonoran.com/news-releases/arizona-sonoran-announces-updated-mineral-resource-estimate-for-the-cactus-project/
Catus PEA, effective date of November 10, 2022: https://arizonasonoran.com/site/assets/files/6218/2022-11-10_-_ps_cactus_mre_tech_report.pdf
Quality Assurance and Quality Control Procedures
Skyline Labs is accredited in accordance with the recognized International Standard ISO/IEC 17025:2005. Their quality management system has been certified as conforming to the requirements defined in the International Standard ISO 9001:2015. The standard operating procedure (SOP) used while processing the ASCU samples was to process samples in groups of 20. Each tray consisted of 18 samples with samples No. 1 and No. 10 repeated as duplicates. The results from each tray were analyzed and any variance in the duplicates of more than 3% would result in the entire tray being re-assayed.
The results of these analyses, including the QA/QC checks, were transmitted to a select set of individuals at ASCU and the qualified persons.
Qualified Persons
The authors of the Technical Report, each of whom is an independent qualified person within the meaning of NI 43-101 are listed below. The responsibilities of the engineering consultants are as follows:
• Ausenco was commissioned by ASCU to manage and coordinate the work related to the PFS and the technical report. Ausenco was also retained to complete the infrastructure design, leach pad design, and to compile the overall cost estimate and financial model.
• AGP and Call & Nicholas (CNI) were commissioned to provide the mining methods for the underground and open pit. AGP provided designs for view berms, waste piles, and the stockpile relocation. Capital and operating costs were included in their scope.
• Samuel Engineering was commissioned to provide the mineral processing and metallurgical testing basis and plant design. Samuel’s scope included the metallurgical test work supervision and analysis, SXEW plant, leaching process, conveyor systems, crushing and stacking system designs. Capital and operating costs for these areas were included as part of their scope.
• Clear Creek managed the drilling programs, hydrogeologic evaluations and environmental field work for the study.
• ALS Geo Resources LLC was retained to provide drilling and resource modelling components of the project.
• Minefill was involved in paste backfill evaluations and trade-off studies. However, this process is not being utilized in the current project scope.
The Qualified Person’s listed below for the technical report have reviewed and verified the contents of this press release as it relates to their responsibilities. By virtue of their education, experience and professional association membership, they are considered Qualified Person as defined by NI 43-101.
Technical aspects of this news release have been reviewed and verified by Dan Johnson, ASCU Director of Projects, who is a qualified person as defined by National Instrument 43-101.
| Qualified Person | Professional Designation | Position | Employer |
| Erin L. Patterson | P.E. | Director of Minerals & Metals | Ausenco Engineering USA South, Inc. |
| Scott C. Elfen | P.E. | Global Lead Geotechnical Services | Ausenco Engineering Canada ULC. |
| R. Douglas Bartlett | RG, CHG, | Principal | Clear Creek Associates, a subsidiary of Geo-Logic Associates |
| Gordon Zurowski | P.Eng. | Principal Mine Engineer | AGP Mining Consultants Inc. |
| Nat Burgio | FAusIMM (CP) | Principal Geologist | AGP Mining Consultants Inc. |
| Todd Carstensen | RM-SME | Principal Mine Engineer | AGP Mining Consultants Inc. |
| Allan L. Schappert | CPG, SME-RM | Principal | ALS Geo Resources LLC |
| James L. Sorensen | FAusIMM | Director | Samuel Engineering, Inc. |
| Paul F. Cicchini | P.E. | President | North Star Geotech LLC |
About Arizona Sonoran Copper Company
(www.arizonasonoran.com | www.cactusmine.com)
ASCU’s objective is to become a mid-tier copper producer with low operating costs and to develop the Cactus and Parks/Salyer Projects that could generate robust returns for investors and provide a long term sustainable and responsible operation for the community and all stakeholders. The Company’s principal asset is a 100% interest in the Cactus Project (former ASARCO, Sacaton mine) which is situated on private land in an infrastructure-rich area of Arizona. Contiguous to the Cactus Project is the Company’s 100%-owned Parks/Salyer deposit that could allow for a phased expansion of the Cactus Mine once it becomes a producing asset. The Company is led by an executive management team and Board which have a long-standing track record of successful project delivery in North America complemented by global capital markets expertise.
For more information
Alison Dwoskin, Director, Investor Relations
647-233-4348
adwoskin@arizonasonoran.com
George Ogilvie, President, CEO and Director
416-723-0458
gogilvie@arizonasonoran.com
Non-IFRS Financial Performance Measures
This news release contains certain non-IFRS measures, including sustaining capital, sustaining costs,
C1 cash costs and AISC. The Company believes that these measures, together with measures determined in accordance with IFRS, provide investors with an improved ability to evaluate the underlying performance of the Company. Non-IFRS measures do not have any standardized meaning prescribed under IFRS, and therefore they may not be comparable to similar measures employed by other companies. The data is intended to provide additional information and should not be considered in isolation or as a substitute for measures of performance prepared in accordance with IFRS.
Cautionary Statement Regarding Estimates of Mineral Resources
This news release uses the terms measured, indicated and inferred mineral resources as a relative measure of the level of confidence in the resource estimate. Readers are cautioned that mineral resources are not mineral reserves and that the economic viability of resources that are not mineral reserves has not been demonstrated. The mineral resource estimate disclosed in this news release may be materially affected by geology, environmental, permitting, legal, title, socio-political, marketing or other relevant issues. The mineral resource estimate is classified in accordance with the Canadian disclosure requirements of Institute of Mining, Metallurgy and Petroleum’s “CIM Definition Standards on Mineral Resources and Mineral Reserves” incorporated by reference into NI 43-101. Under NI 43-101, estimates of inferred mineral resources may not form the basis of feasibility or pre-feasibility studies or economic studies except for preliminary economic assessments. Readers are cautioned not to assume that further work on the stated resources will lead to mineral reserves that can be mined economically.
Forward-Looking Statements
This news release contains “forward-looking statements” and/or “forward-looking information” (collectively, “forward-looking statements”) within the meaning of applicable securities legislation. All statements, other than statements of historical fact, are forward-looking statements. Generally, forward-looking statements can be identified by the use of forward-looking terminology such as “plans”, “expect”, “is expected”, “in order to”, “is focused on” (a future event), “estimates”, “intends”, “anticipates”, “believes” or variations of such words and phrases or statements that certain actions, events or results “may”, “could”, “would”, or the negative connotation thereof. In particular, statements regarding ASCU’s future operations, future exploration and development activities or other development plans constitute forward-looking statements. By their nature, statements referring to mineral reserves or mineral resources constitute forward-looking statements. Forward-looking statements in this news release include, but are not limited to statements with respect to the results (if any) of further exploration work to define and expand or upgrade mineral resources and reserves at ASCU’s properties; the anticipated exploration, drilling, development, construction and other activities of ASCU and the result of such activities; the mineral resources and mineral reserves estimates of the Cactus Project (and the assumptions underlying such estimates); the ability of exploration work (including drilling) to accurately predict mineralization; the ability of management to understand the geology and potential of the Cactus Project; the focus of the 2024 drilling program at the Cactus Project including the Parks/Salyer deposit and MainSpring property; the ability to generate additional drill targets; the ability of ASCU to complete its exploration objectives in 2024 in the timing contemplated (if at all); the completion and timing for the filing of the Technical Report; the timing and ability of ASCU to produce a preliminary economic assessment (including the MainSpring property) (if at all); the timing and ability of ASCU to produce the Nuton Case PFS (if at all); the scope of any future technical reports and studies conducted by ASCU; the ability to realize upon mineralization in a manner that is economic; the impact of bringing the MainSpring property into the mine plan; the ability and timing of ASCU to commence operations (if at all); the robust economics and opportunity represented by the Cactus Project; the ability of ASCU’s operations to be among the top 10 copper operations in Arizona and the US (if at all); the impact of the NutonTM technologies on ASCU operations and cost relating to same; the impact of the relationship with Nuton on ASCU and its operations and any other information herein that is not a historical fact.
ASCU considers its assumptions to be reasonable based on information currently available but cautions the reader that their assumptions regarding future events, many of which are beyond the control of the Company, may ultimately prove to be incorrect since they are subject to risks and uncertainties that affect ASCU, its properties and business. Such risks and uncertainties include, but not limited to, the global economic climate, developments in world commodity markets, changes in commodity prices (particularly prices of copper), risks relating to fluctuations in the Canadian dollar and other currencies relative to the US dollar, risks relating to capital market conditions and ASCU’s ability to access capital on terms acceptable to ASCU for the contemplated exploration and development at the Company’s properties, changes in exploration, development or mining plans due to exploration results and changing budget priorities of ASCU or its joint venture partners, the effects of competition in the markets in which ASCU operates, results of further exploration work, the ability to continue exploration and development at ASCU’s properties, the ability to successfully apply the NutonTM technologies in ASCU’s properties, the impact of the NutonTM technologies on ASCU operations and cost relating to same, the timing and ability for ASCU to prepare and complete the Nuton Case PFS and the costs relating to same, errors in geological modelling, changes in any of the assumptions underlying the PFS, the ability to expand operations or complete further exploration activities, the ability to obtain regulatory approvals, the impact of changes in the laws and regulations regulating mining exploration, development, closure, judicial or regulatory judgments and legal proceedings, operational and infrastructure risks and the additional risks described in ASCU’s most recently filed Annual Information Form, annual and interim management’s discussion and analysis, copies of which are available on SEDAR+ (www.sedarplus.ca) under ASCU’s issuer profile. ASCU’s anticipation of and success in managing the foregoing risks could cause actual results to differ materially from what is anticipated in such forward-looking statements.
Although management considers the assumptions contained in forward-looking statements to be reasonable based on information currently available to it based on information available at the date of preparation, those assumptions may prove to be incorrect. There can be no assurance that these forward-looking statements will prove to be accurate, as actual results and future events could differ materially from those anticipated in such statements. Accordingly, readers should not place undue reliance on forward-looking statements and are urged to carefully consider the foregoing factors as well as other uncertainties and risks outlined in ASCU’s public disclosure record.
ASCU disclaims any obligation to update any forward-looking statements, whether as a result of new information, future events or results or otherwise, except as required by law.
VANCOUVER, CANADA (January 15, 2024) – Aldebaran Resources Inc. (“Aldebaran” or the”Company“) (TSX-V: ALDE, OTCQX: ADBRF) is pleased to announce that it has entered into a collaboration agreement with Nuton LLC, a Rio Tinto Venture (“Nuton”) to evaluate the use of Nuton’s proprietary primary sulphide leaching technologies on the Altar copper-gold project, located in San Juan, Argentina.
Under the terms of the agreement, Aldebaran will deliver samples representing various styles of mineralization from the Altar project to Nuton. Nuton will then complete detailed mineralogical analyses of each sample before placing the material into columns. Samples will be placed in columns with a height of 1 m, each under different controlled Nuton operating conditions. It is expected that the full results will be available approximately one year after the columns are loaded. Test work is currently anticipated to commence in H1 2024.
As part of the agreement, Aldebaran has granted exclusivity to Nuton in the area of novel, patented or trade secret leaching technologies, for a period of one year starting on the agreement date of January 9, 2024. The parties will share the cost of the test program with Aldebaran covering the cost of preparation and shipping of the samples to Nuton, and Nuton paying for the costs of metallurgical test work.
John E. Black, Chief Executive Officer of Aldebaran, commented: “We’re happy to collaborate with Nuton to evaluate the potential use of their sulphide leaching technology at the Altar project. While sulphide leaching isn’t necessary to move the Altar project forward, it could positively impact the project’s economics, if successful.”
Adam Burley, Chief Executive Officer of Nuton, commented “We are pleased to announce this collaboration agreement with Aldebaran. Nuton has a wide range of potential use cases. At Altar we are encouraged by the potential of Nuton to unlock copper resources in a project with substantial scale potential and in a way that is more environmentally efficient than conventional processes”
ON BEHALF OF THE ALDEBARAN BOARD
“John Black”
John Black
Chief Executive Officer and Director
Please click here and subscribe to receive future news releases: https://aldebaranresources.com/contact/subscribe/
For further information, please consult our website at www.aldebaranresources.com or contact:
Ben Cherrington
Manager, Investor Relations
Phone: +1 347 394-2728 or +44 7538 244 208
Email: ben.cherrington@aldebaranresources.com
About Nuton
Nuton is an innovative venture that aims to help grow Rio Tinto’s copper business. At the core of Nuton is a portfolio of proprietary copper leach related technologies and capability – a product of almost 30 years of research and development. Nuton offers the potential to economically unlock copper from primary sulfide resources worldwide through leaching, achieving market-leading recovery rates, contributing to an increase in copper production from copper bearing waste and tailings, and achieving higher copper recoveries on oxide and transitional material. One of the key differentiators of Nuton is the potential to produce the world’s lowest carbon footprint copper while having at least one Positive Impact at each of our deployment sites, across our five pillars: water, energy, land, materials and society.
About Aldebaran Resources Inc.
Aldebaran is a mineral exploration company that was spun out of Regulus Resources Inc. in 2018 and has the same core management team. Aldebaran holds a 60% interest in the Altar copper-gold project in San Juan Province, Argentina and can earn an additional 20% interest in the project by completing a further US$25 million in expenditures at Altar over the next three years. The Altar project hosts multiple porphyry copper-gold deposits with potential for additional discoveries. Altar forms part of a cluster of world-class porphyry copper deposits which includes Los Pelambres (Antofagasta Minerals), El Pachón (Glencore), and Los Azules (McEwen Copper). In March 2021 the Company announced an updated mineral resource estimate for Altar, prepared by Independent Mining Consultants Inc. and based on the drilling completed up to and including 2020 (independent technical report prepared by Independent Mining Consultants Inc., Tucson, Arizona, titled “Technical Report, Estimated Mineral Resources, Altar Project, San Juan Province, Argentina“, dated March 22, 2021 – see news release dated March 22, 2021).
Forward-Looking Statements
Certain statements regarding Aldebaran, including management’s assessment of future-plans and operations, may constitute forward-looking statements under applicable securities laws and necessarily involve known and unknown risks and uncertainties, most of which are beyond Aldebaran’s control. Often, but not always, forward-looking statements or information can be identified by the use of words such as “plans”, “expects” or “does not expect”, “is expected”, “budget”, “scheduled”, “estimates”, “forecasts”, “intends”, “anticipates” or “does not anticipate” or “believes” or variations of such words and phrases or statements that certain actions, events or results “may”, “could”, “would”, “might” or “will” be taken, occur or be achieved.
Specifically, and without limitation, all statements included in this press release that address activities, events or developments that Aldebaran expects or anticipates will or may occur in the future, including the proposed exploration and development of the Altar project described herein, and management’s assessment of future plans and operations and statements with respect to the completion of the anticipated exploration and development programs, may constitute forward-looking statements under applicable securities laws and necessarily involve known and unknown risks and uncertainties, most of which are beyond Aldebaran’s control. These risks may cause actual financial and operating results, performance, levels of activity and achievements to differ materially from those expressed in, or implied by, such forward-looking statements. Although Aldebaran believes that the expectations represented in such forward-looking statements are reasonable, there can be no assurance that such expectations will prove to be correct. The forward-looking statements contained in this press release are made as of the date hereof and Aldebaran does not undertake any obligation to publicly update or revise any forward-looking statements or information, whether as a result of new information, future events or otherwise, unless so required by applicable securities law.
Neither the TSX Venture Exchange nor its Regulation Services Provider (as that term is defined in policies of the TSX Venture Exchange) accepts responsibility for the adequacy or accuracy of this release.
